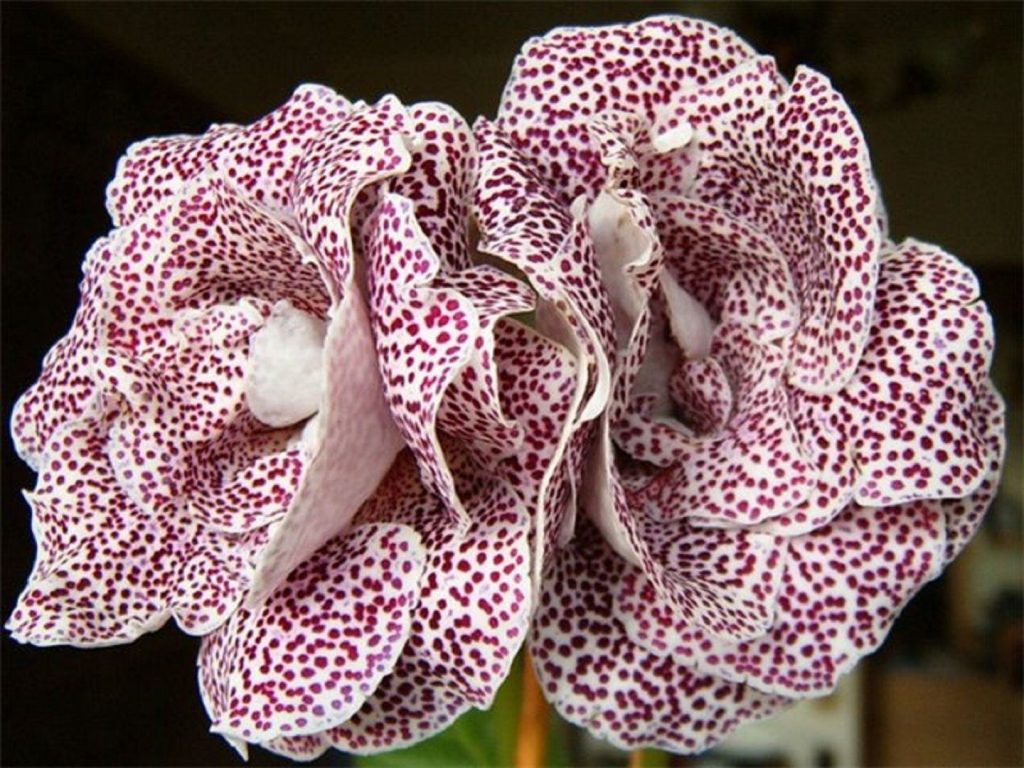
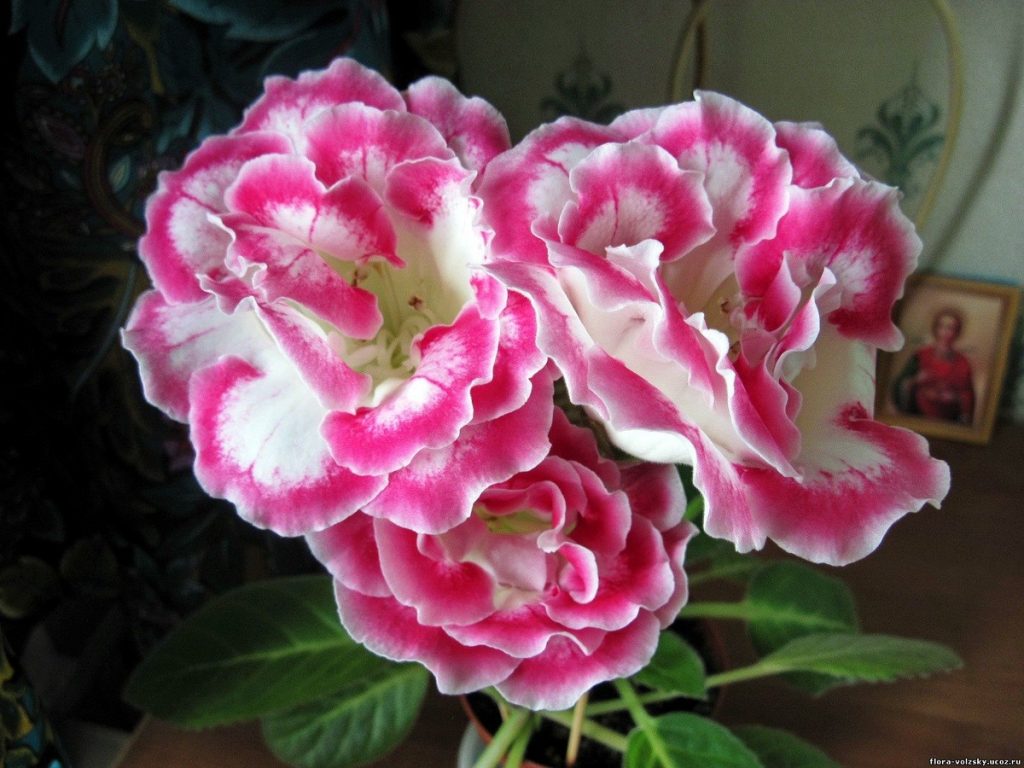
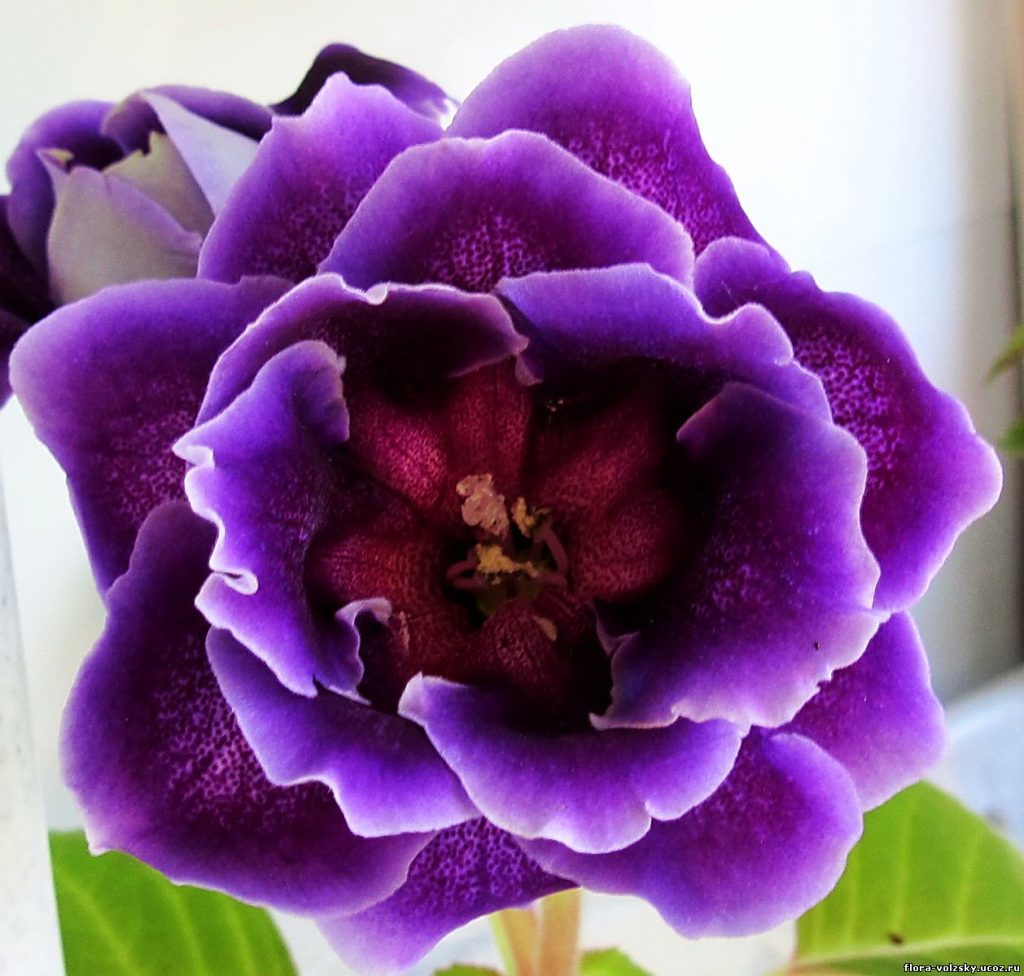
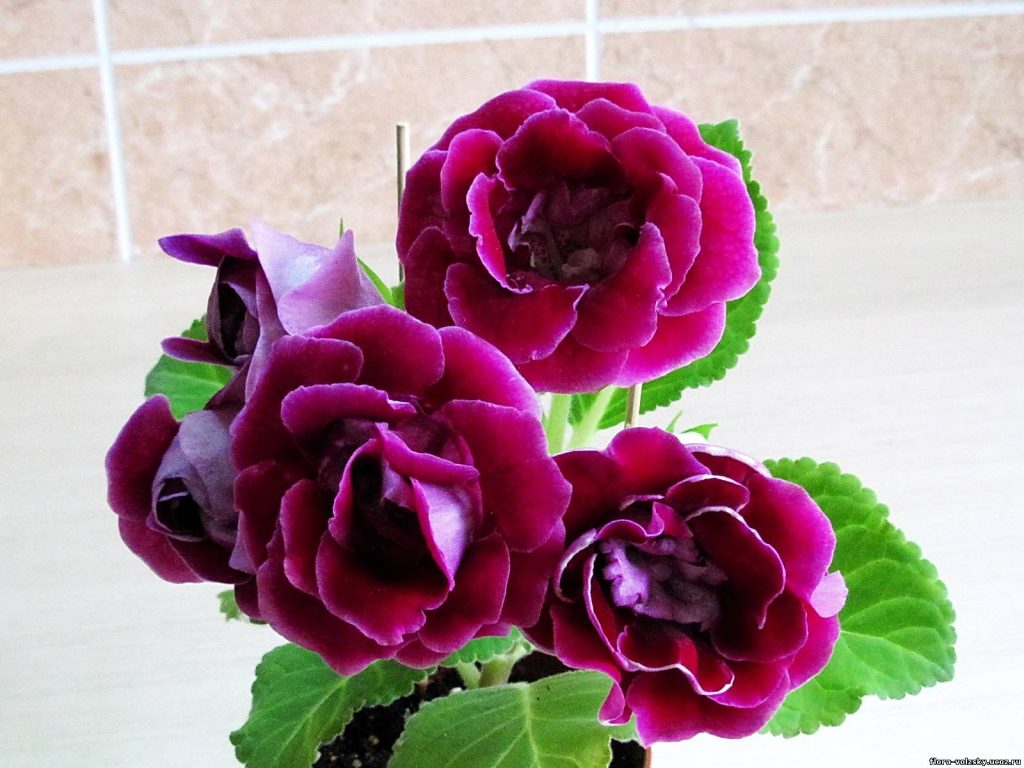
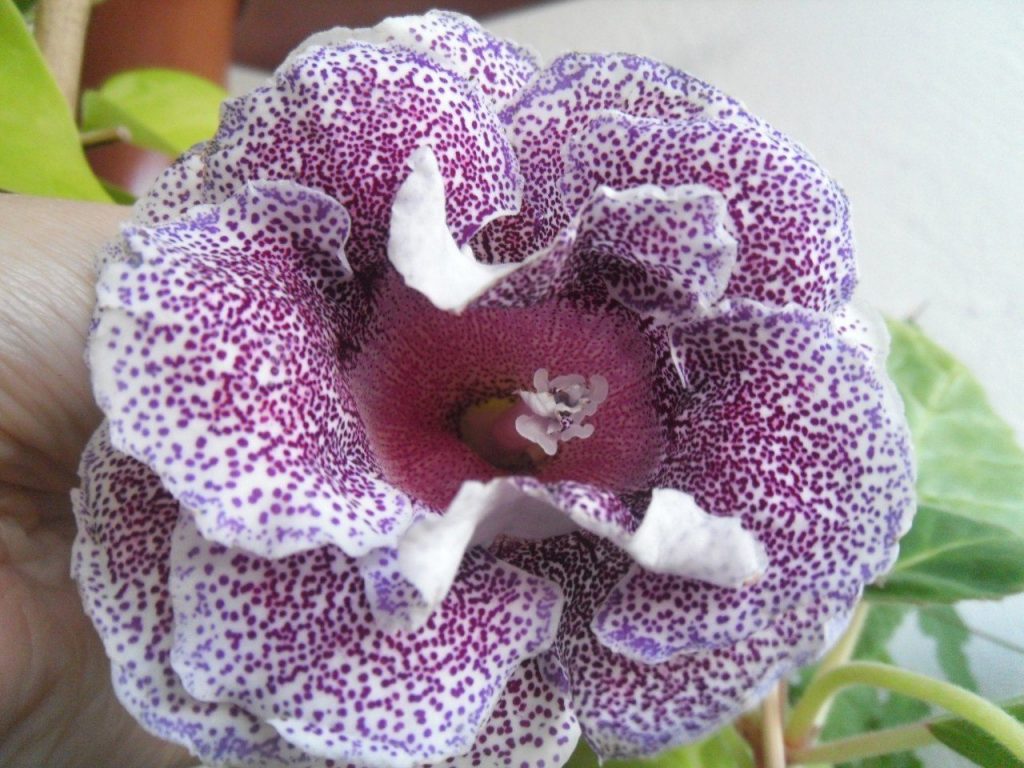
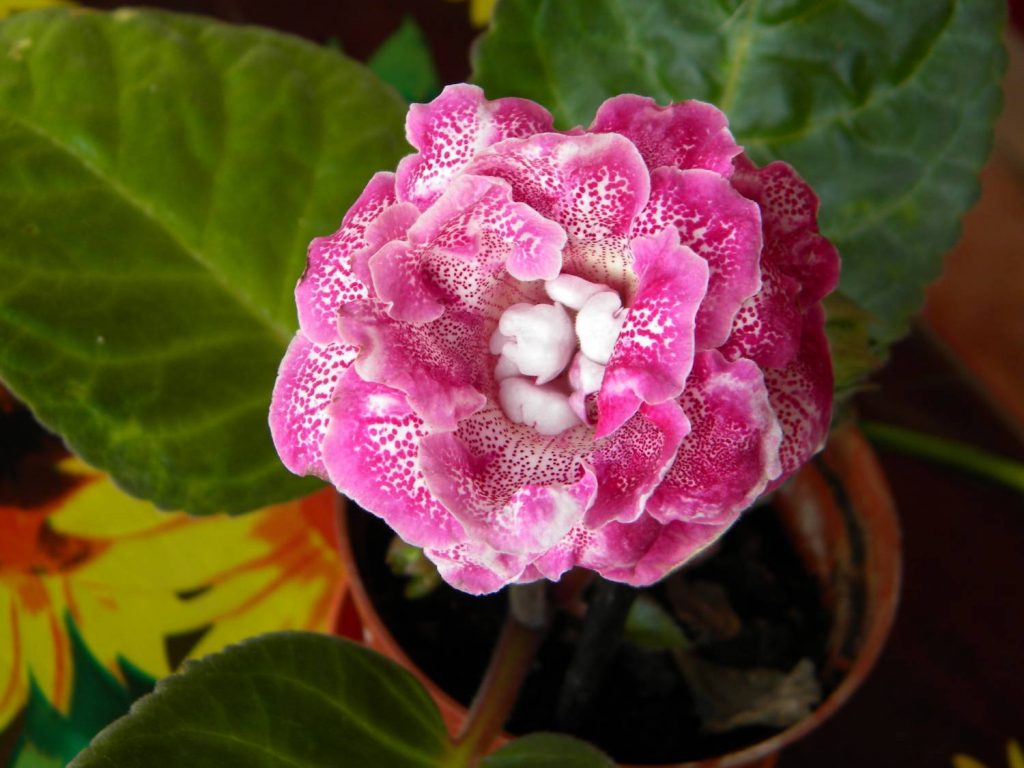
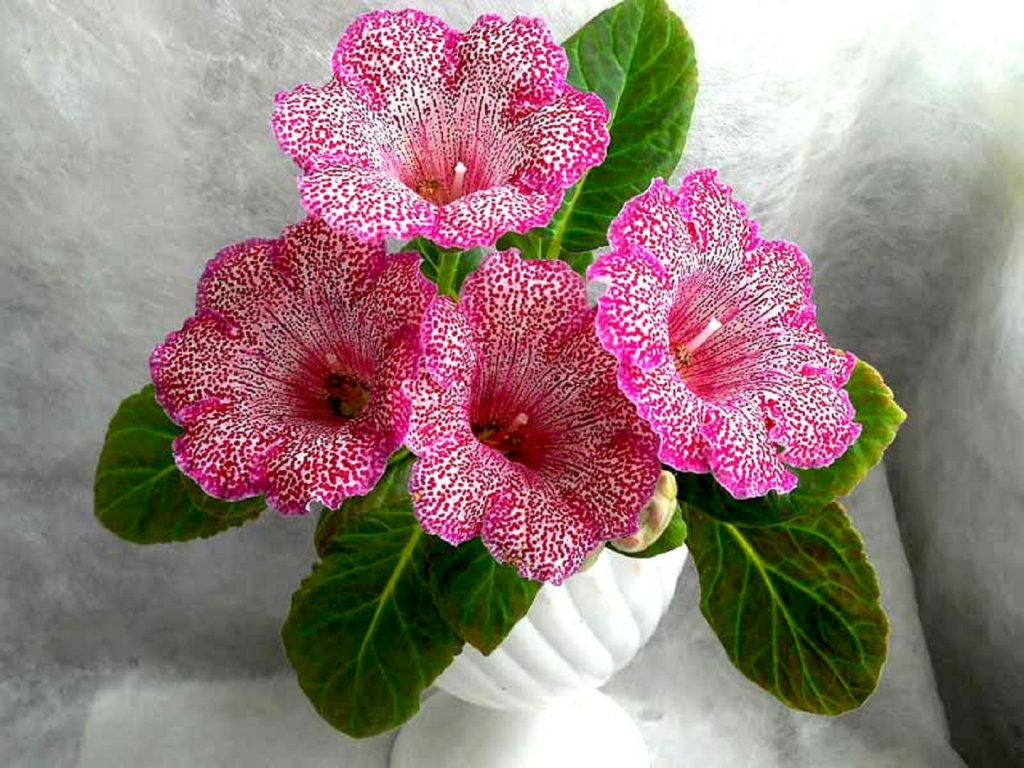
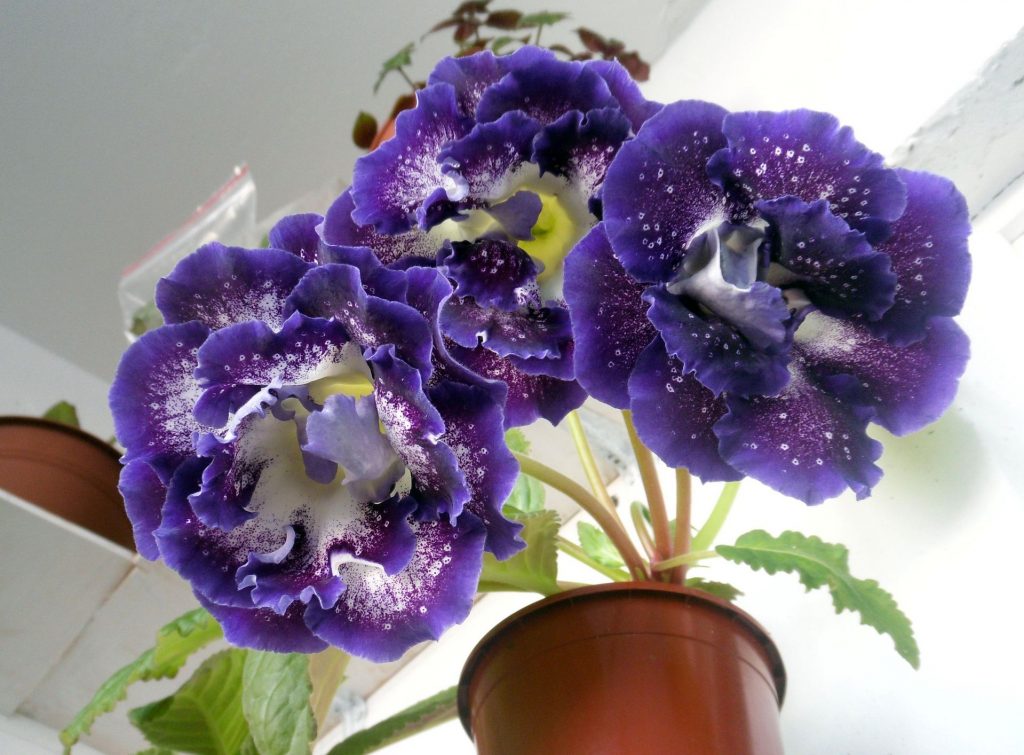
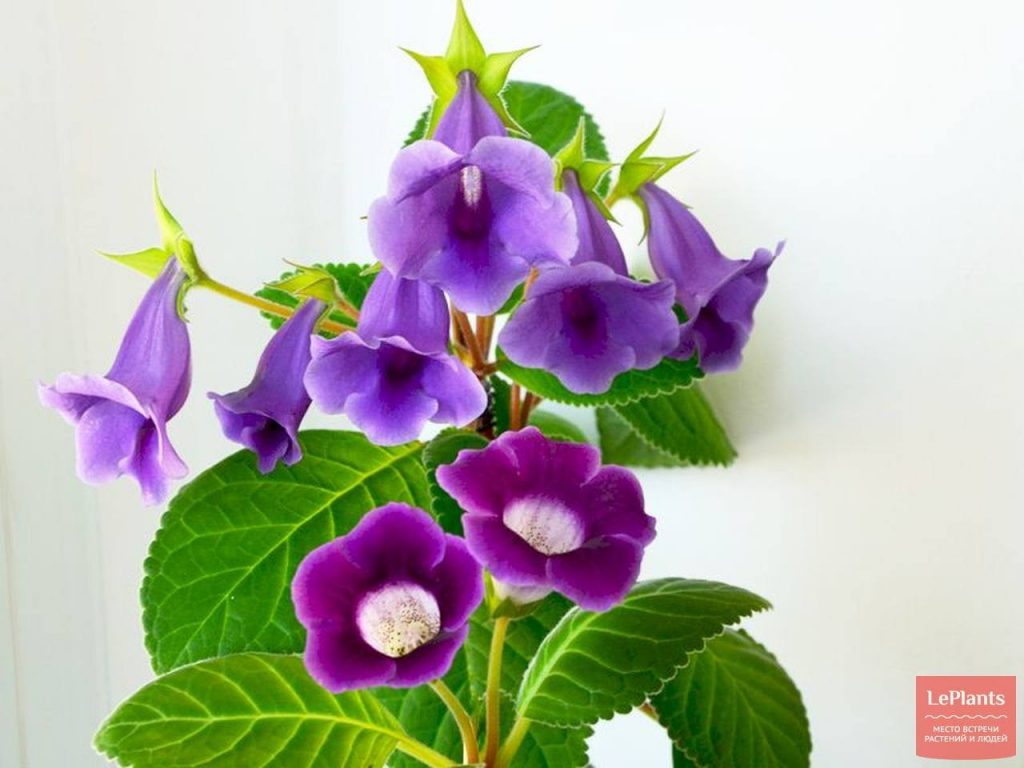
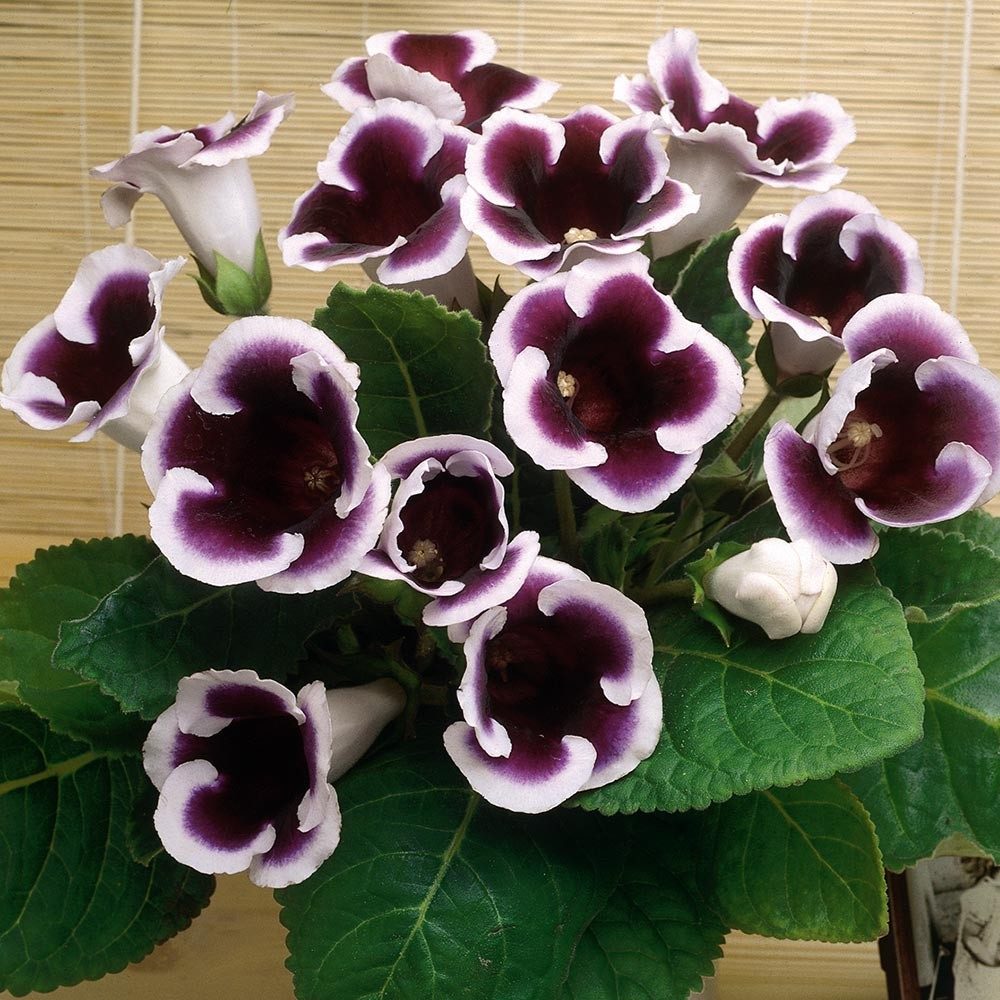
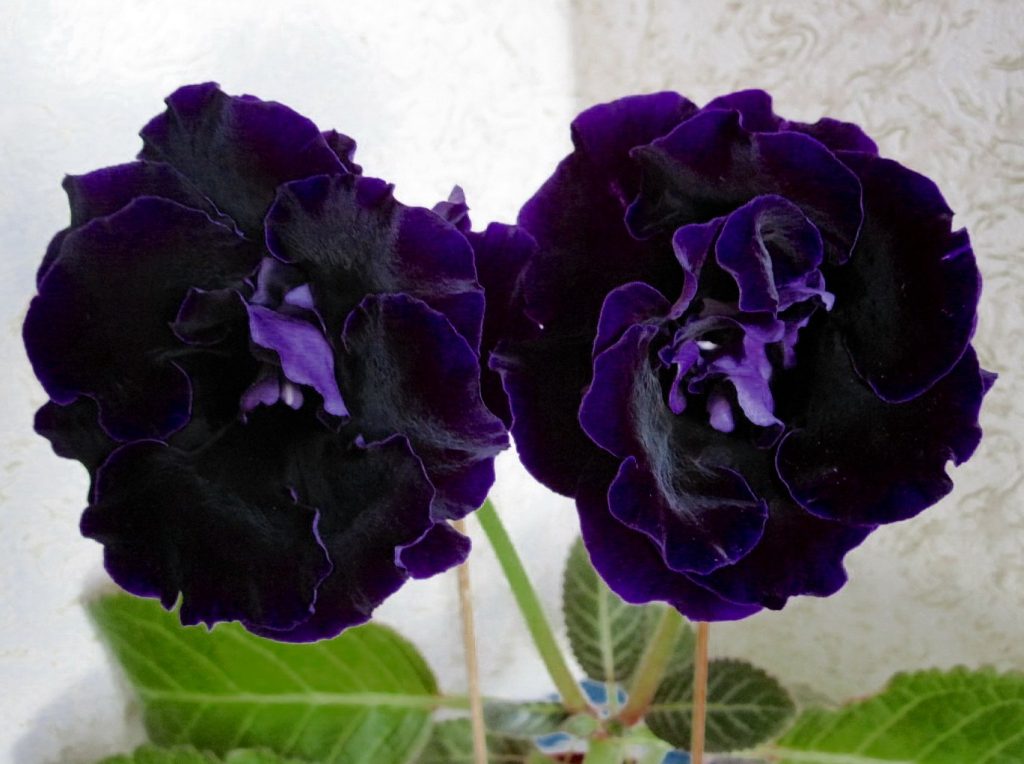
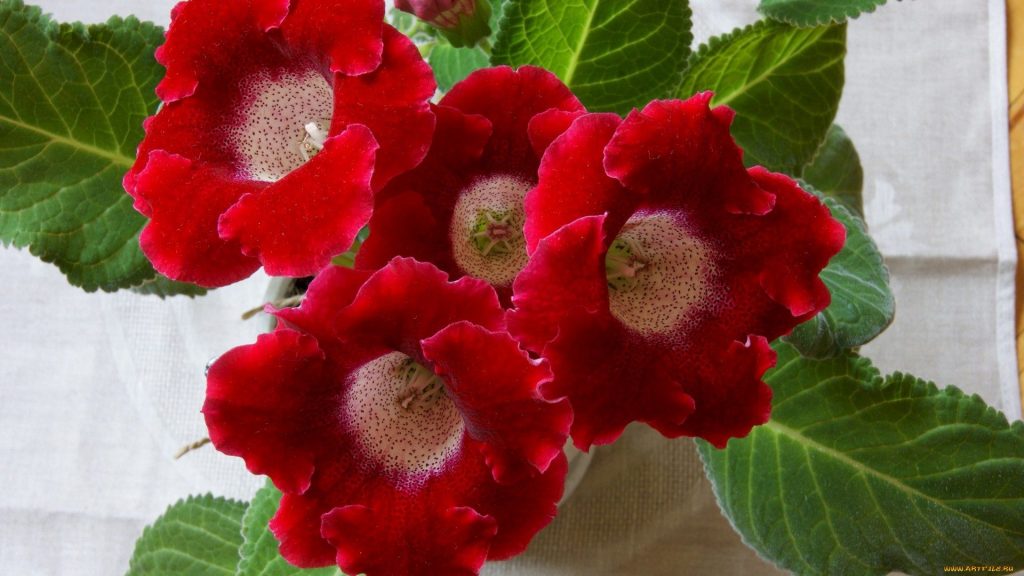
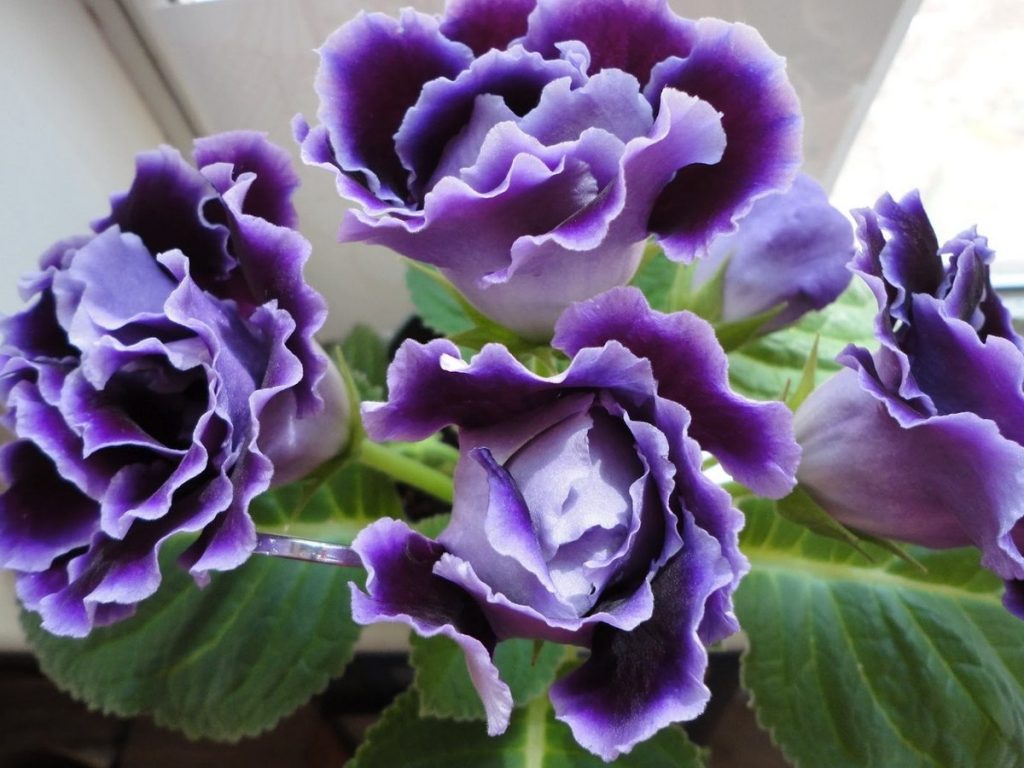
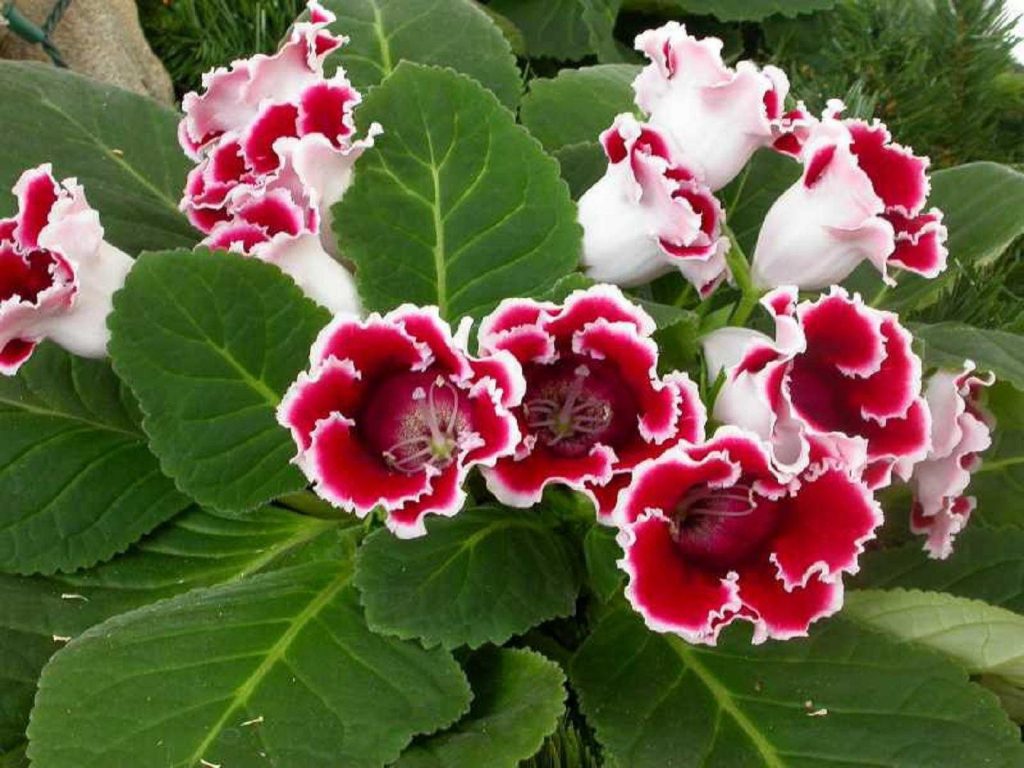
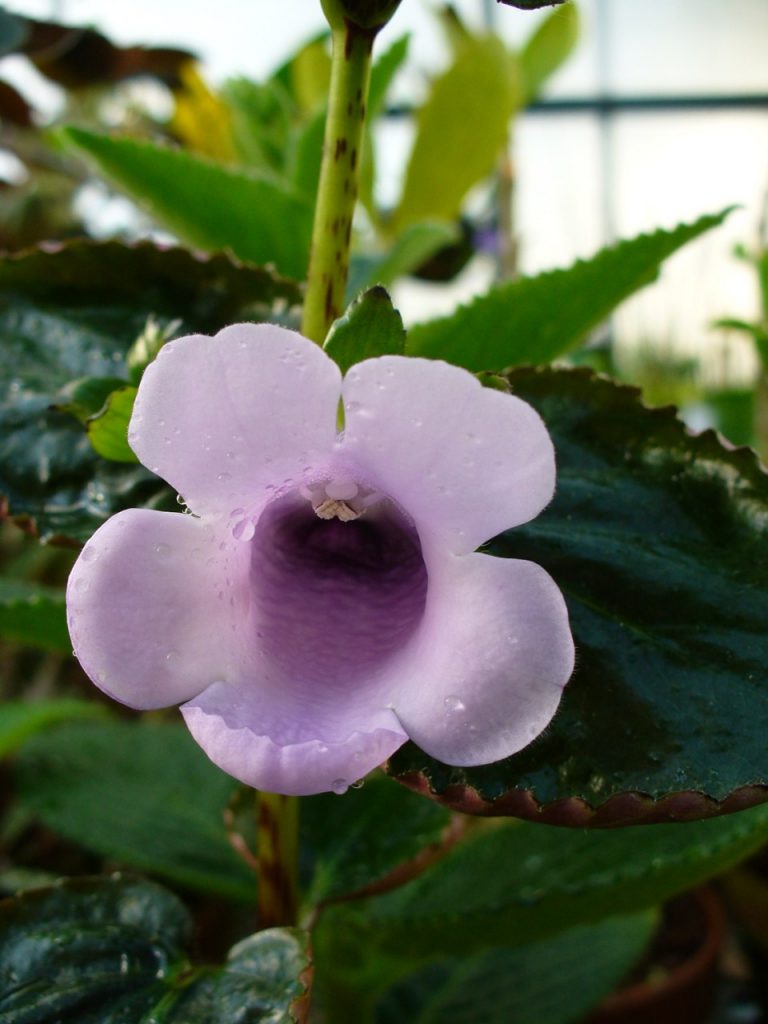
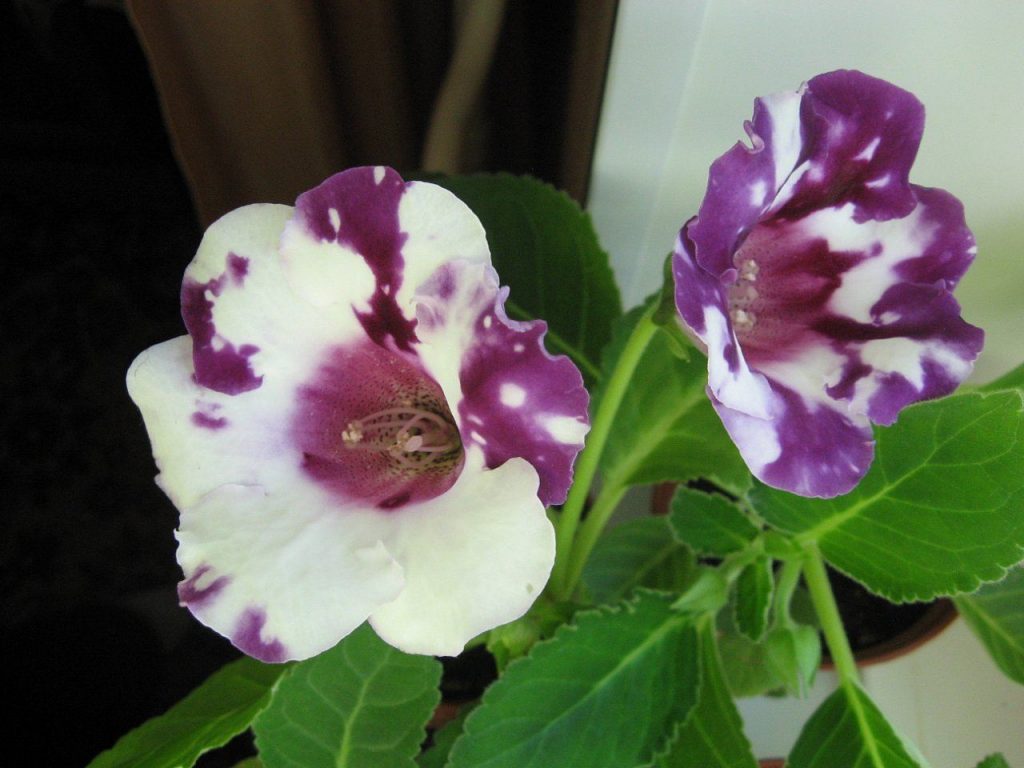
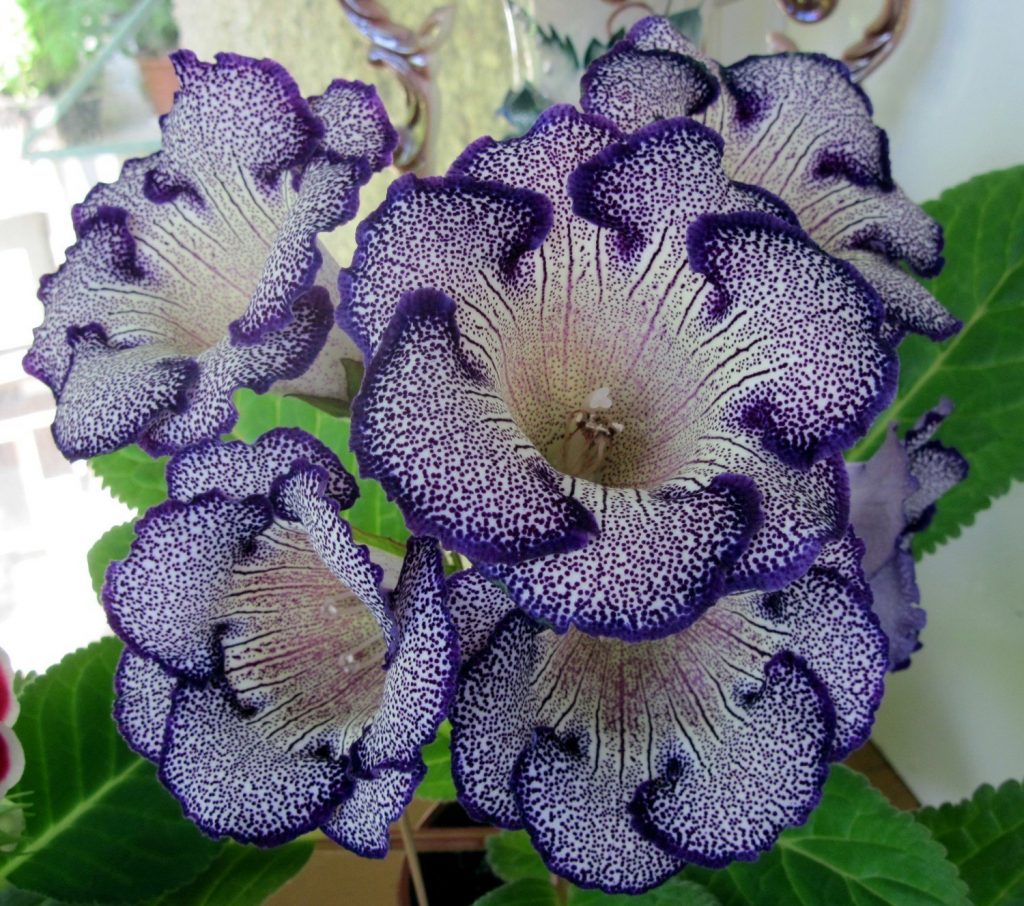
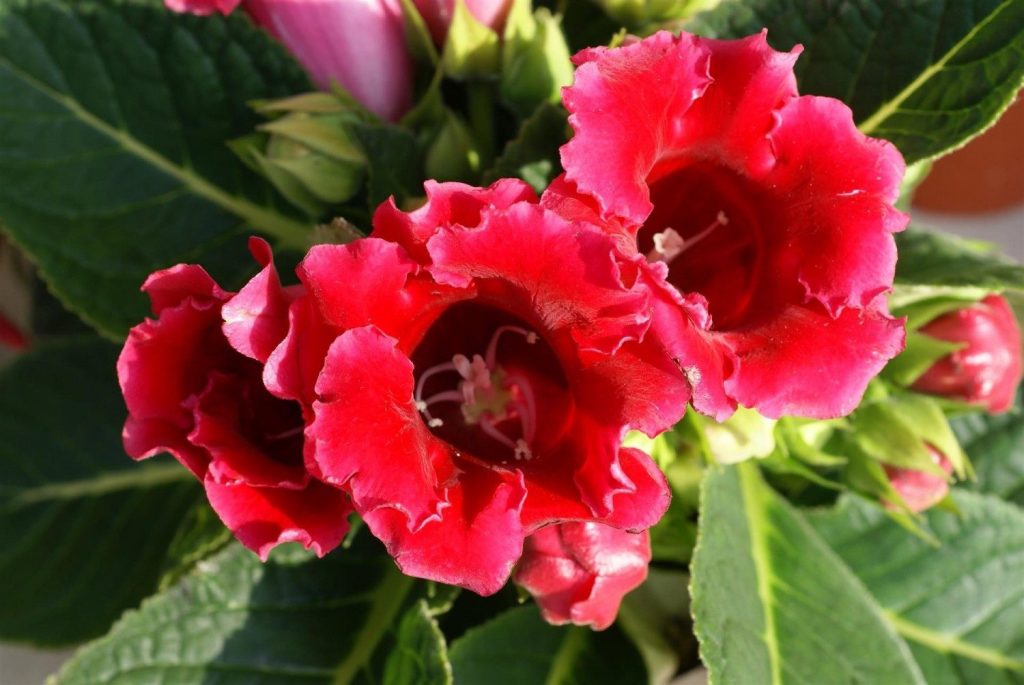
Gloxinia or sinningia is a beautiful plant, belonging to the Hesnerian family. Its homeland is the tropics of South and Central America. The flower is quite unpretentious. The only difficulty you may encounter is storing the tubers of a plant.
Gloxinia Description
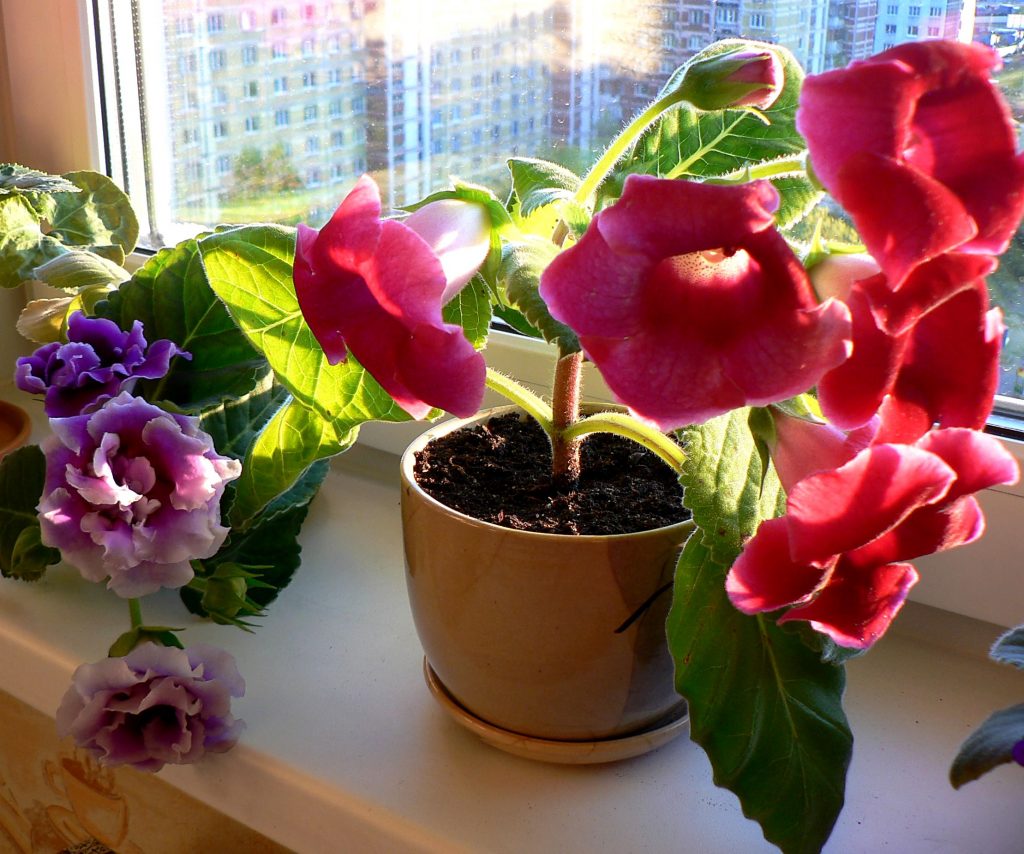
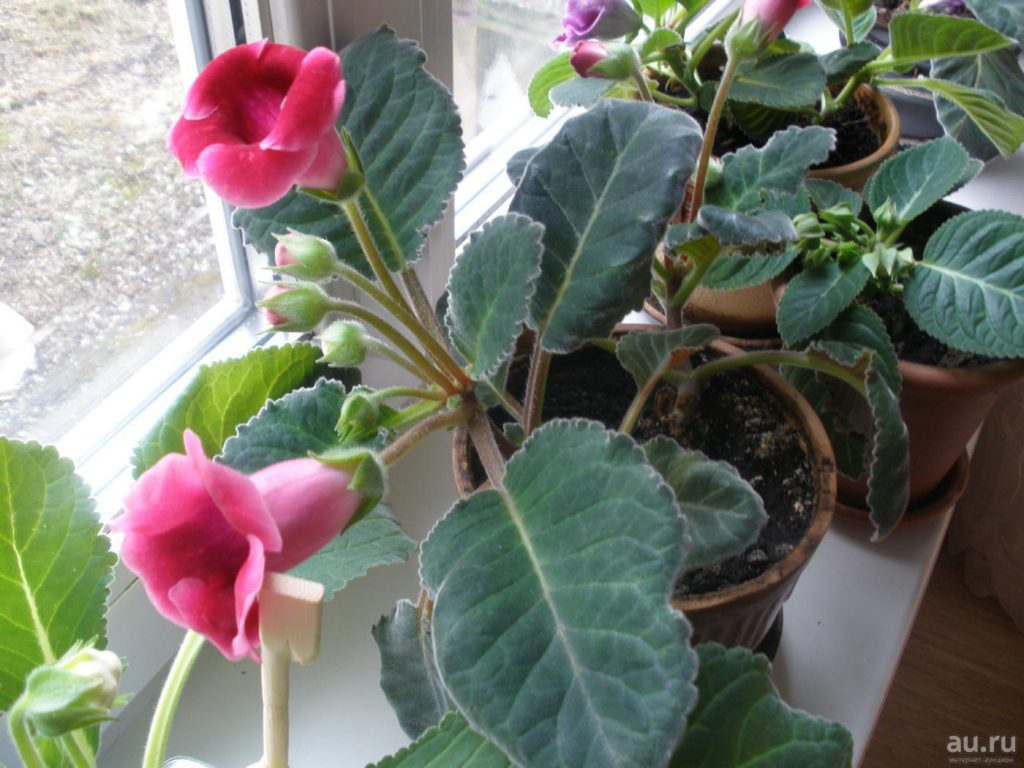
Gloxinia is a herbaceous plant with short stems and fleshy shoots. The leaves of the plant are rather large dark green. They have an ovoid shape and are covered with a fluff from above.
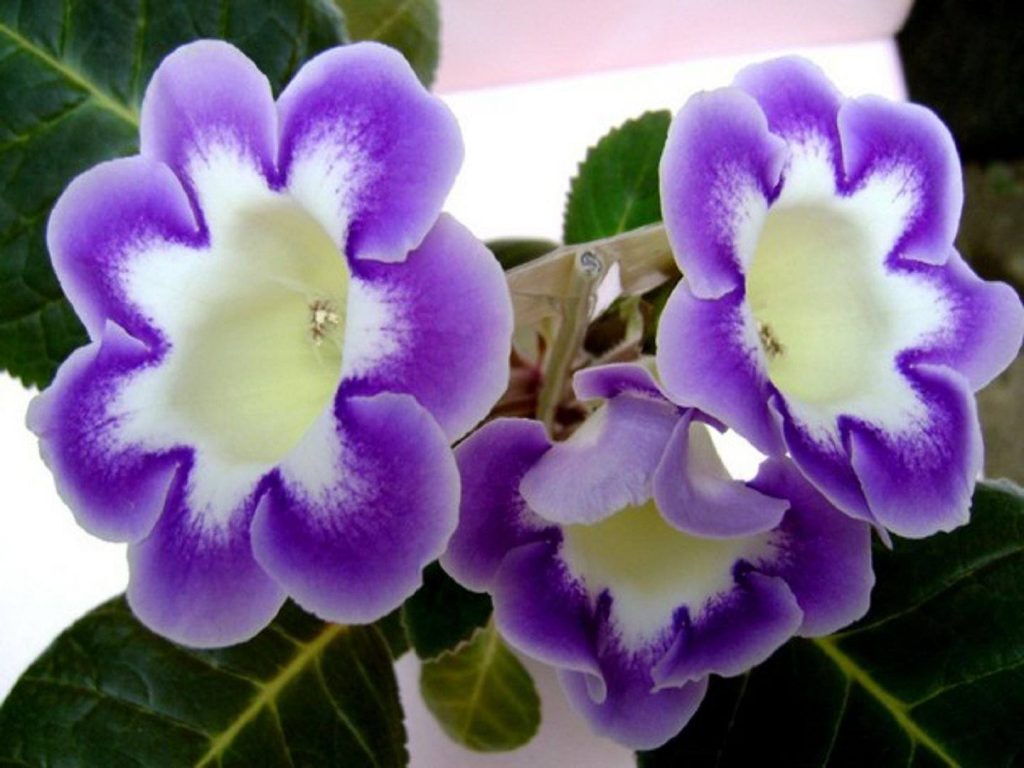
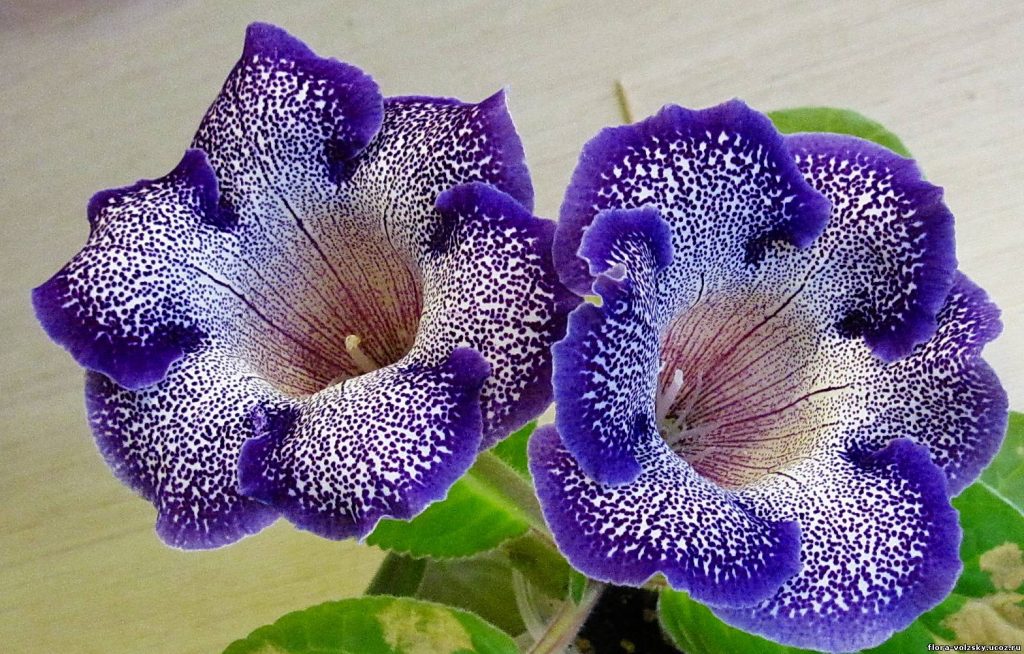
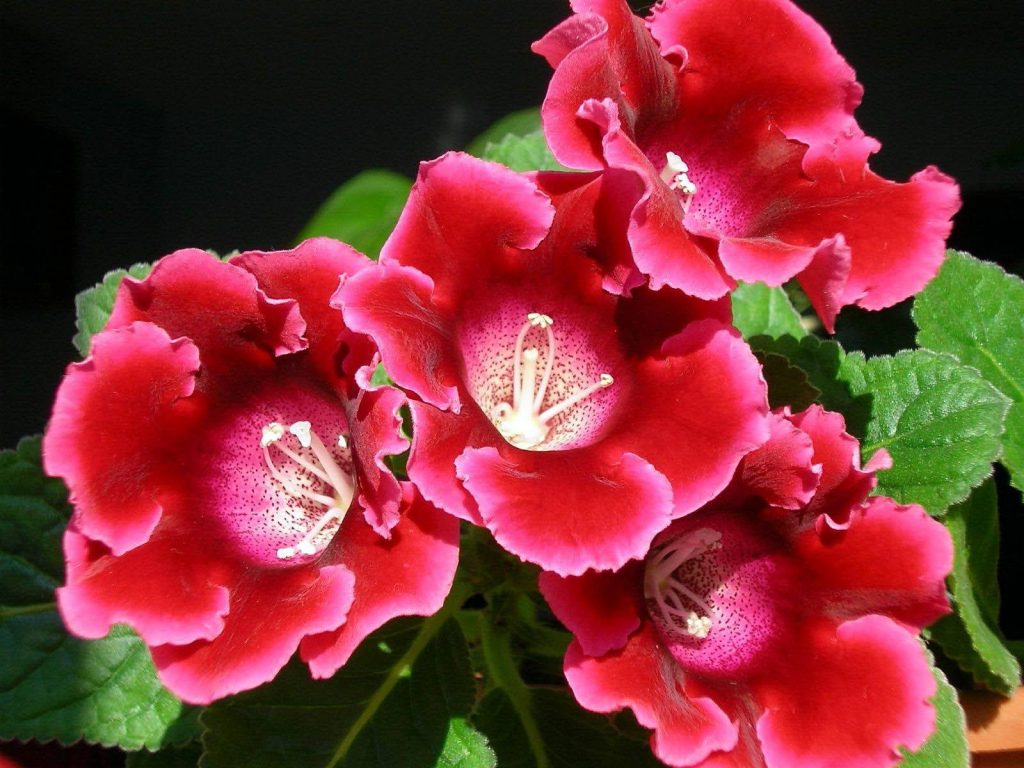
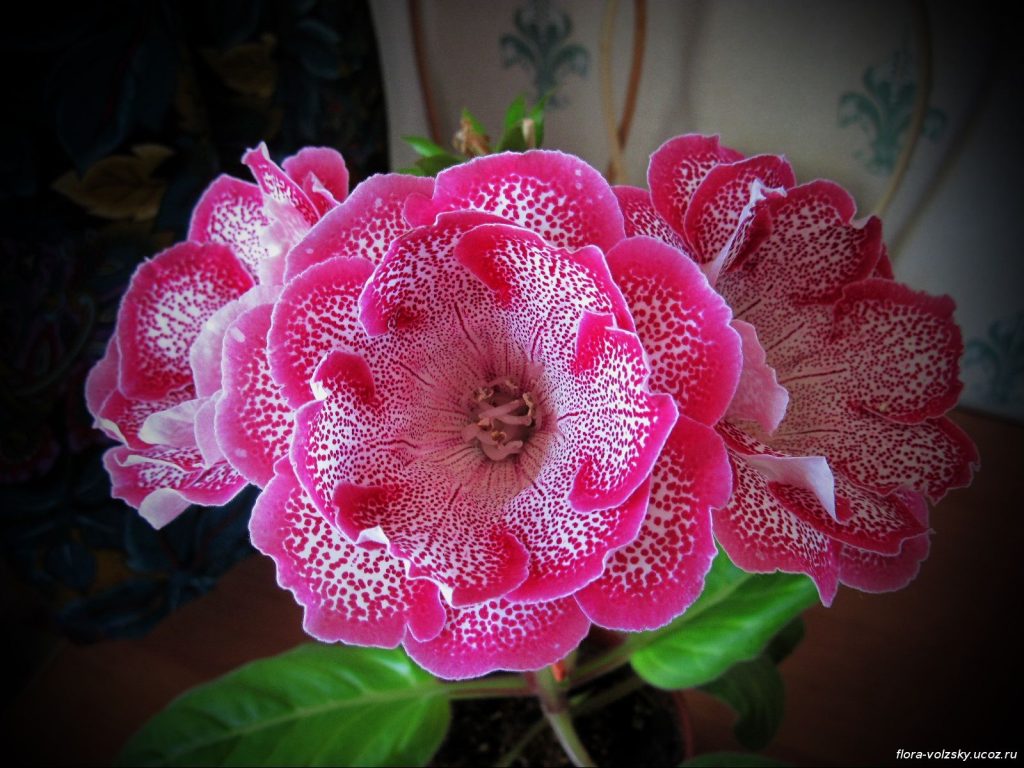
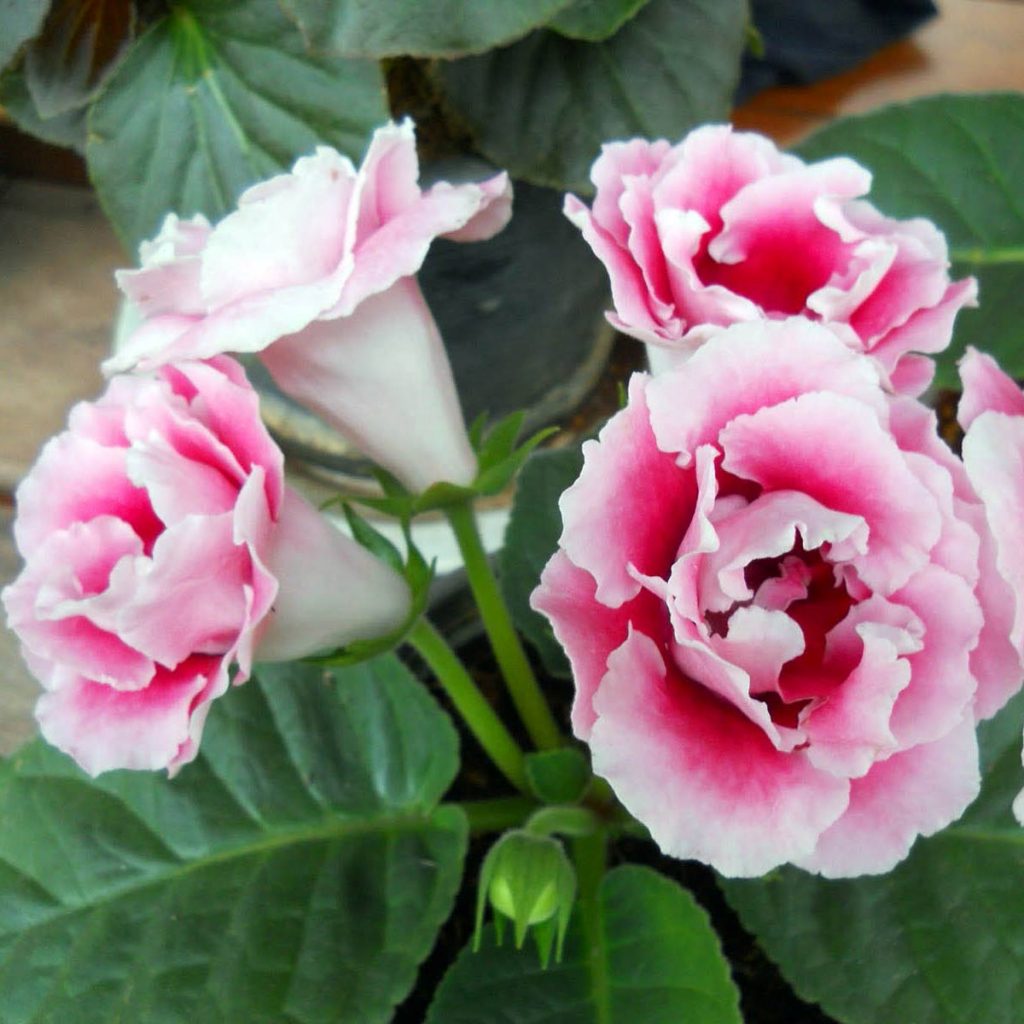
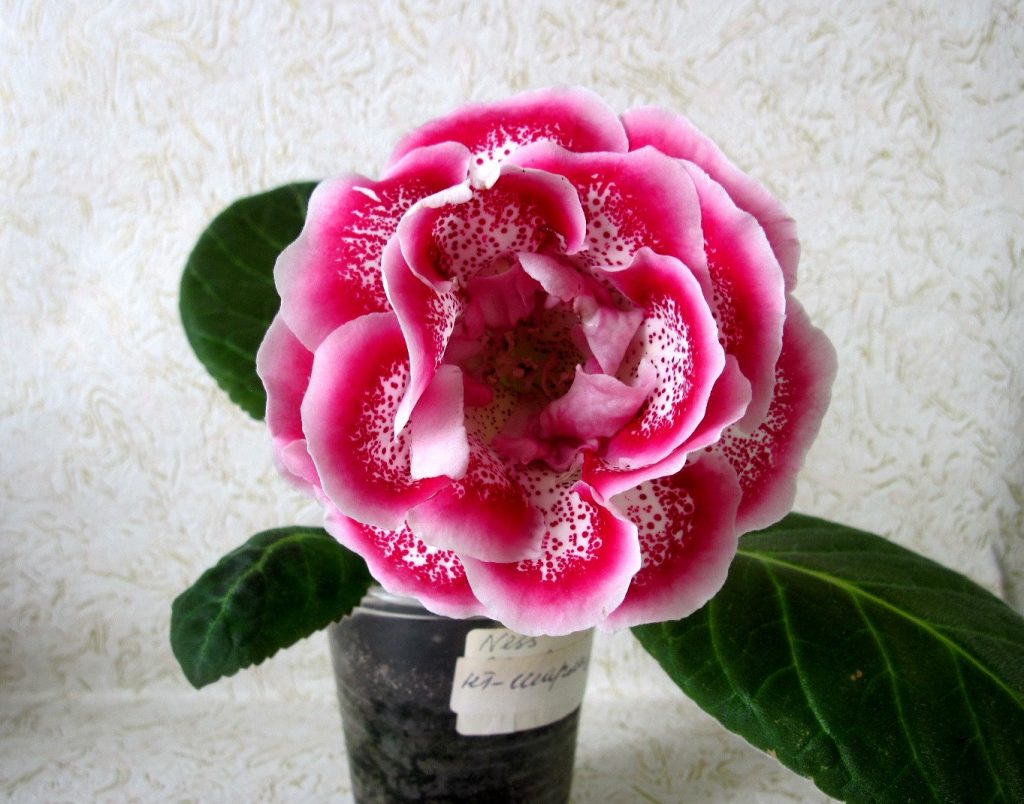
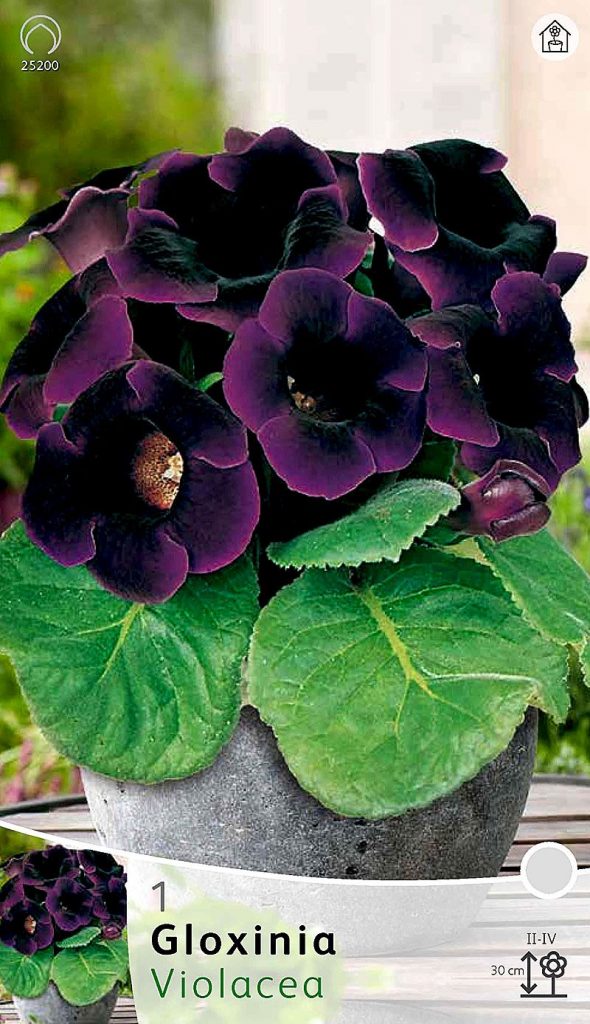
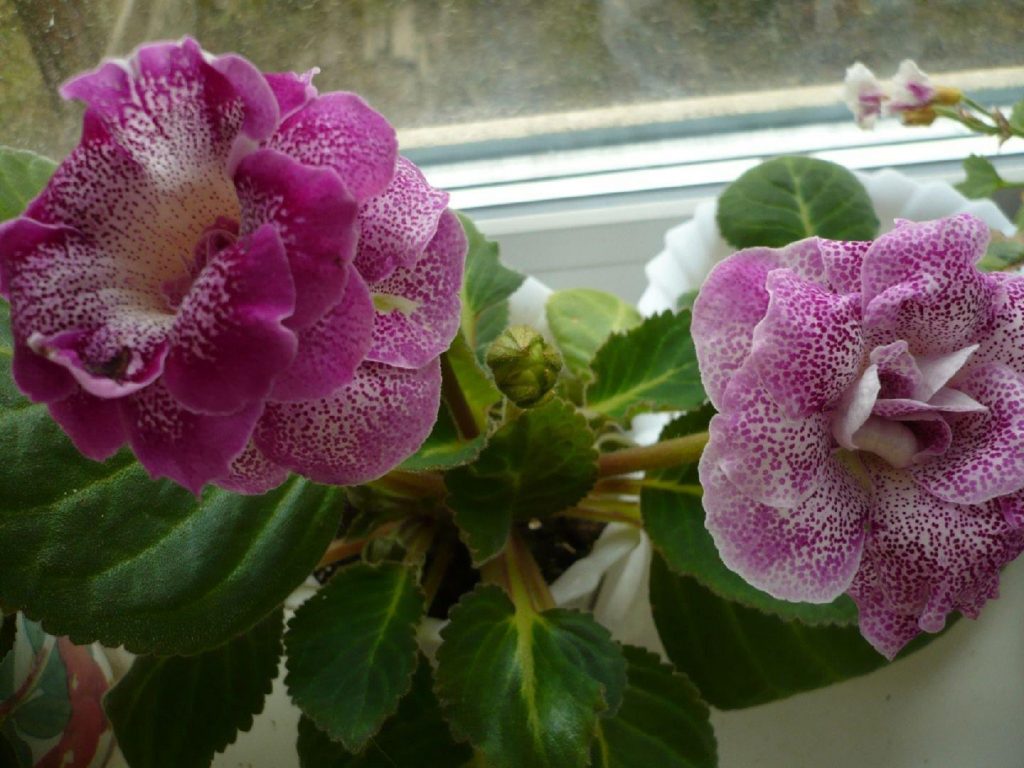
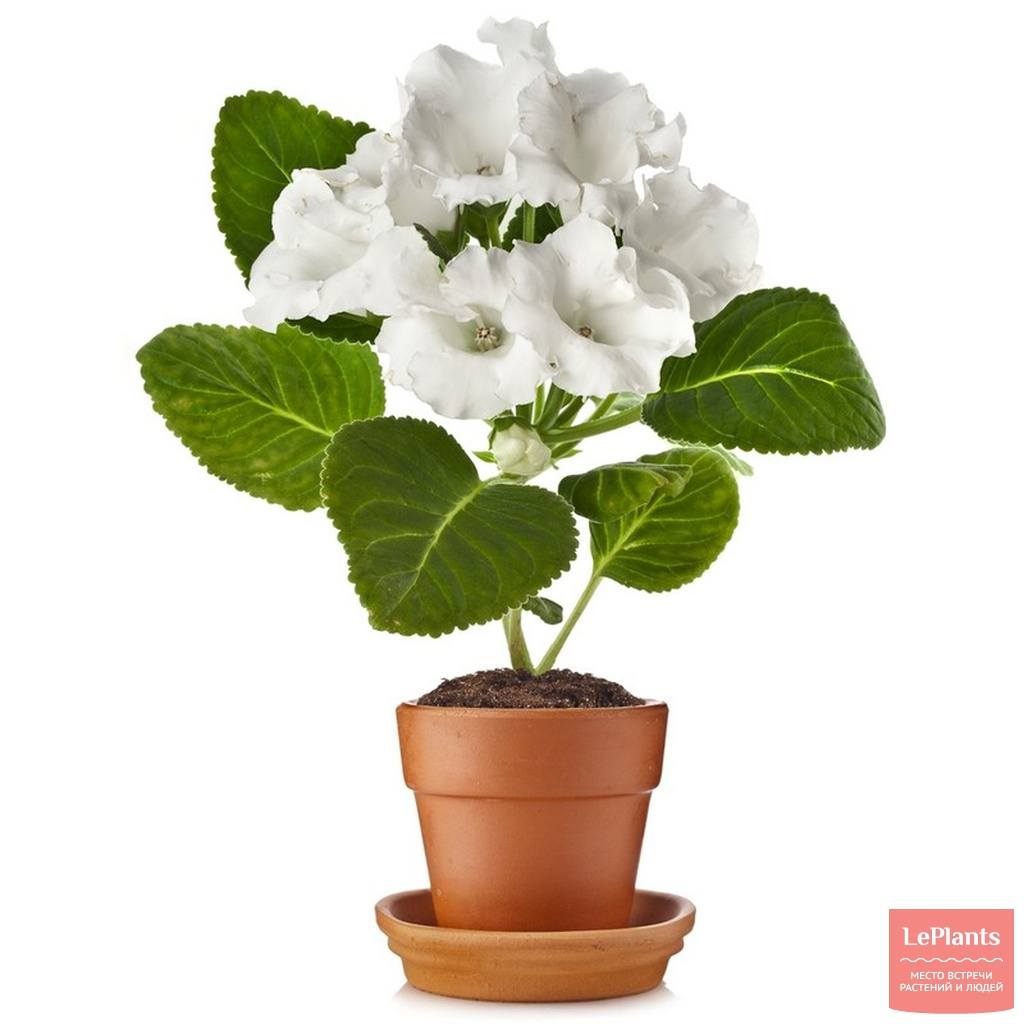
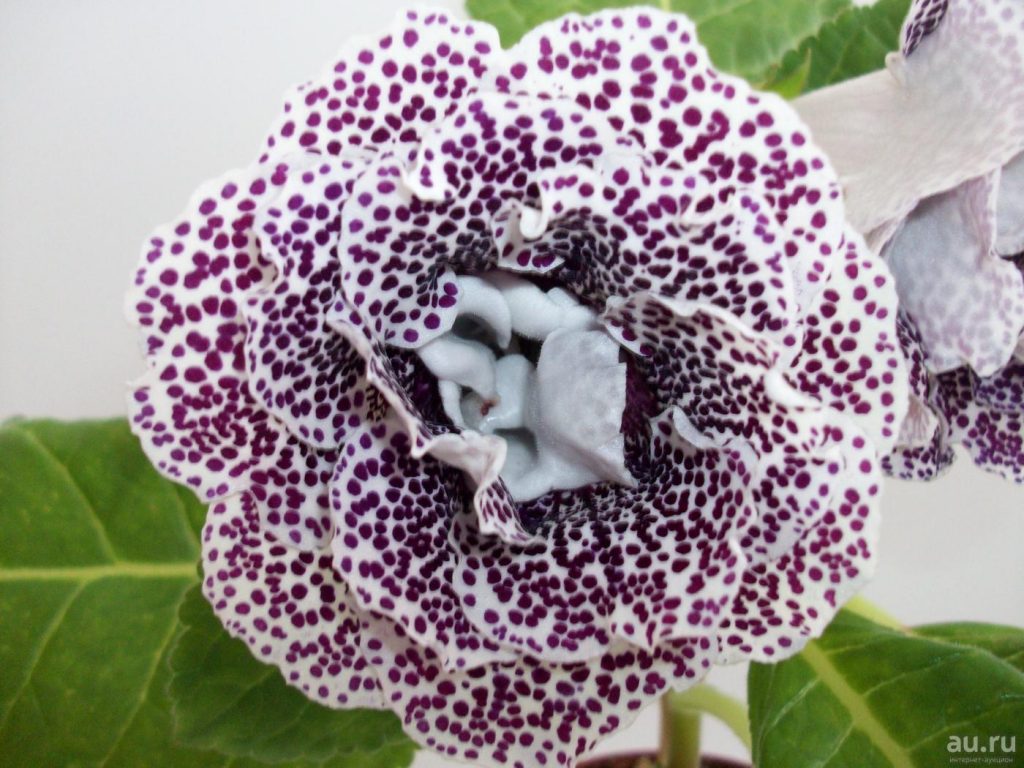
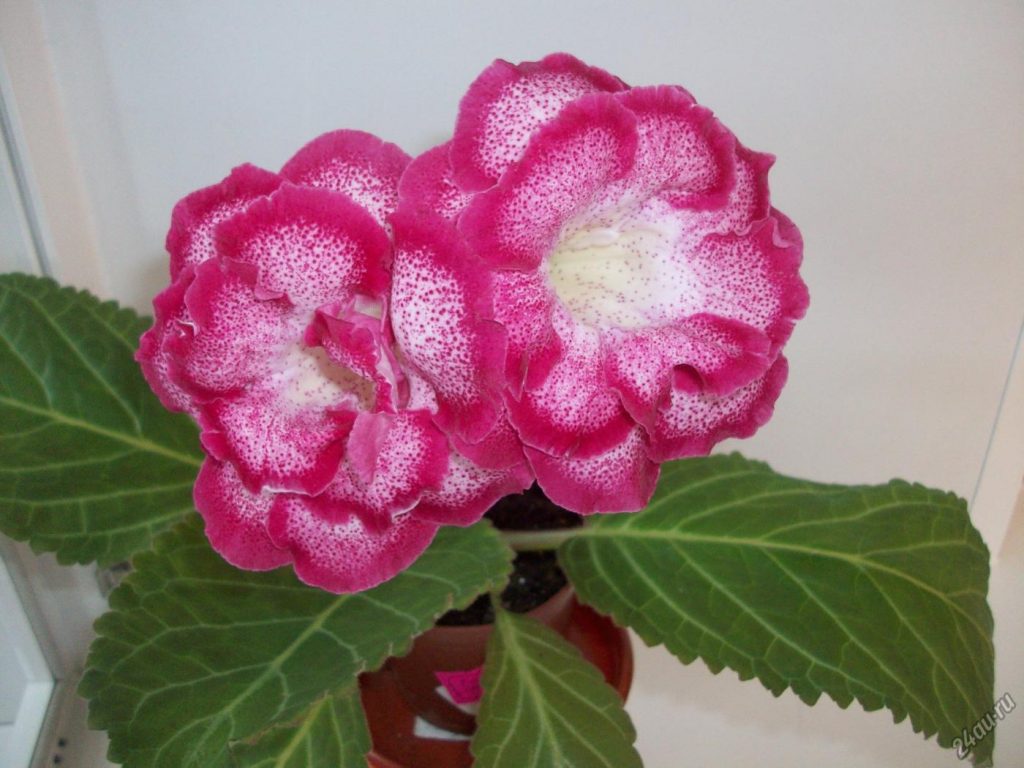
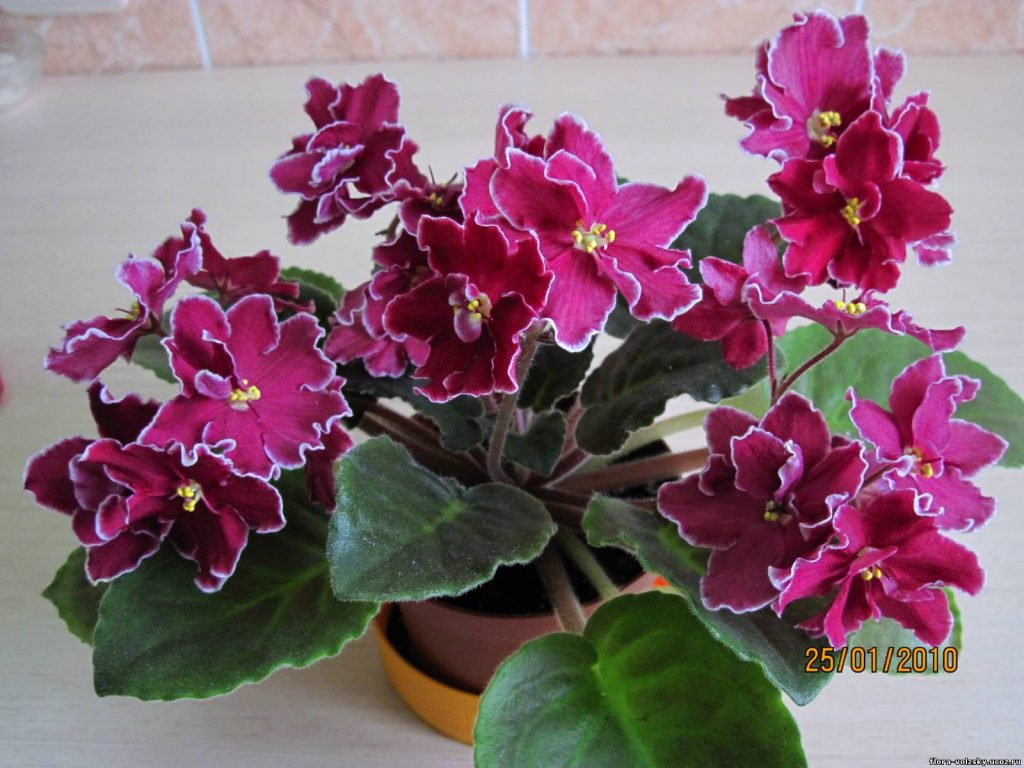
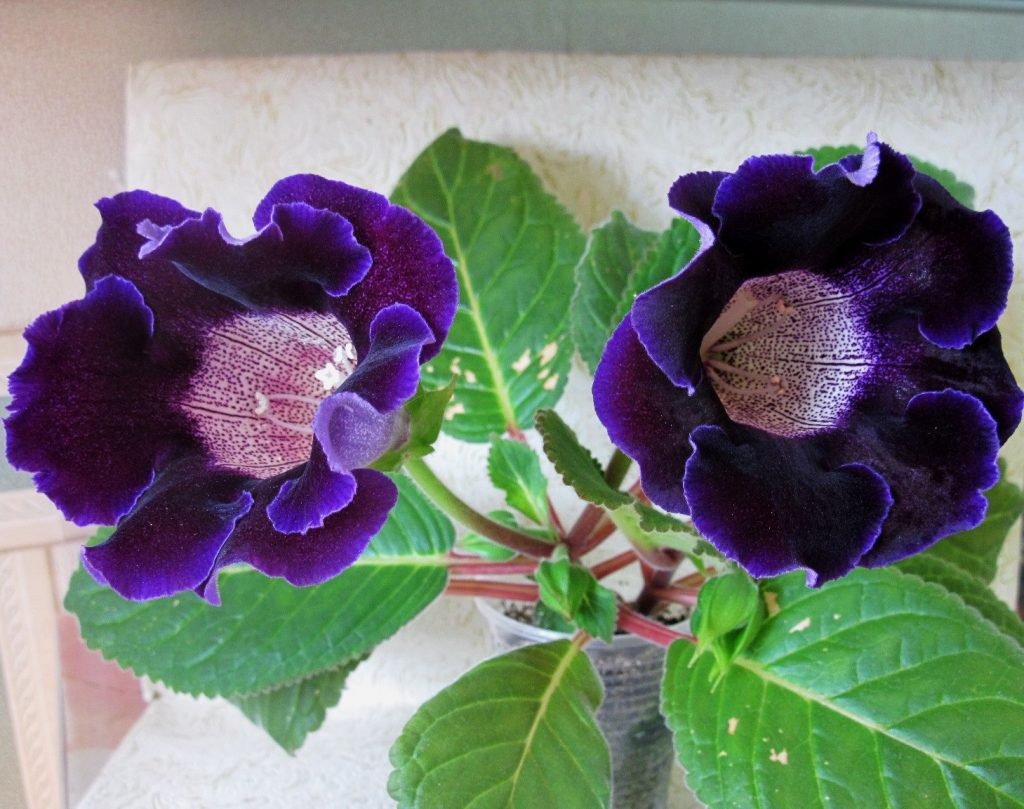
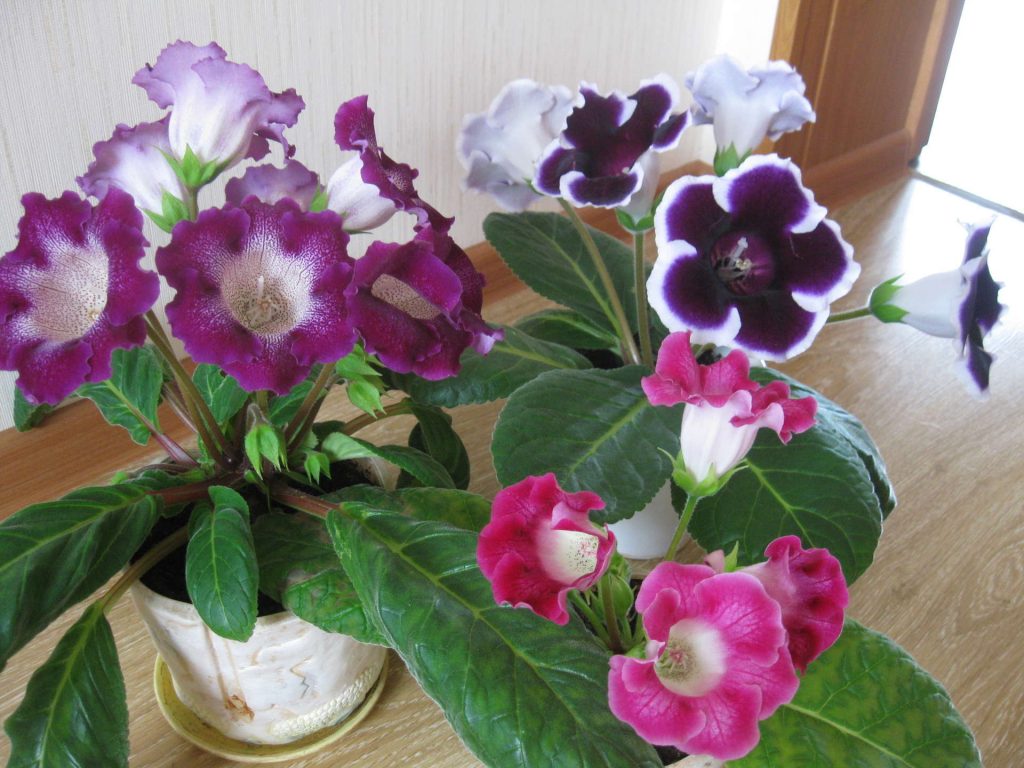
Gloxinia flowers also have velvety petals and grow up to 12 cm in diameter. Externally, the flower resembles a bell with corrugated edges. Gloxinia colors can be varied: from white or pale pink to purple and dark burgundy.
If the plant is properly maintained, it blooms regularly, releasing from 8 to 40 flowers at a time. Duration of flowering is approximately 3 months (usually gloxinia blooms from March to June).
When buying gloxinia, pay attention to the number of still unblown buds. With good care, such a flower can bloom for you for a few more months.
Gloxinia: home care
This flowering plant likes good lighting. However, the plant should be protected from the sun. The temperature in the room where the flower is located should be around 20-22 degrees. When the temperature drops below 17 degrees, the plant can get sick and even die.
The sill in the southern part of the house with diffused light will be an ideal place for a flower. The main thing is that there is not hot and not dry.
Water gloxinia need often, but in small portions. For this ideal water at room temperature. It should be poured into the pan, as the plant does not tolerate moisture on the flowers and leaves.
At the end of the flowering period of gloxinia, the number of waterings should be gradually reduced, thus preparing the plant for a rest period. During the appearance of buds and flowering, gloxinia needs high humidity. However, you can not spray the plant.
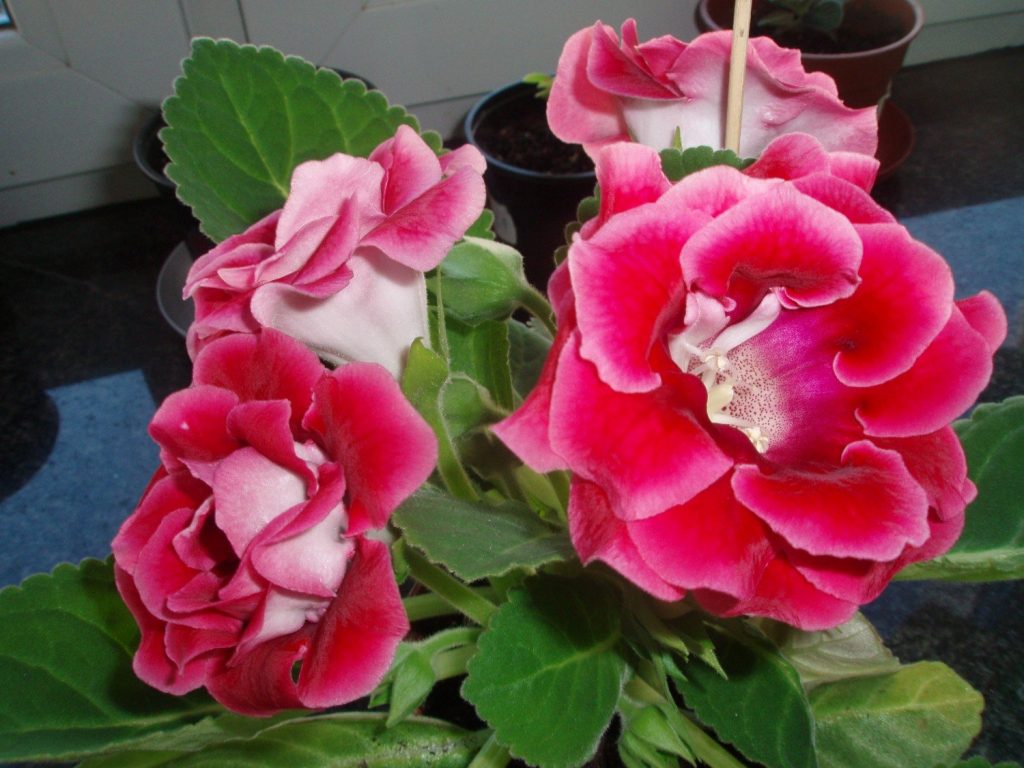
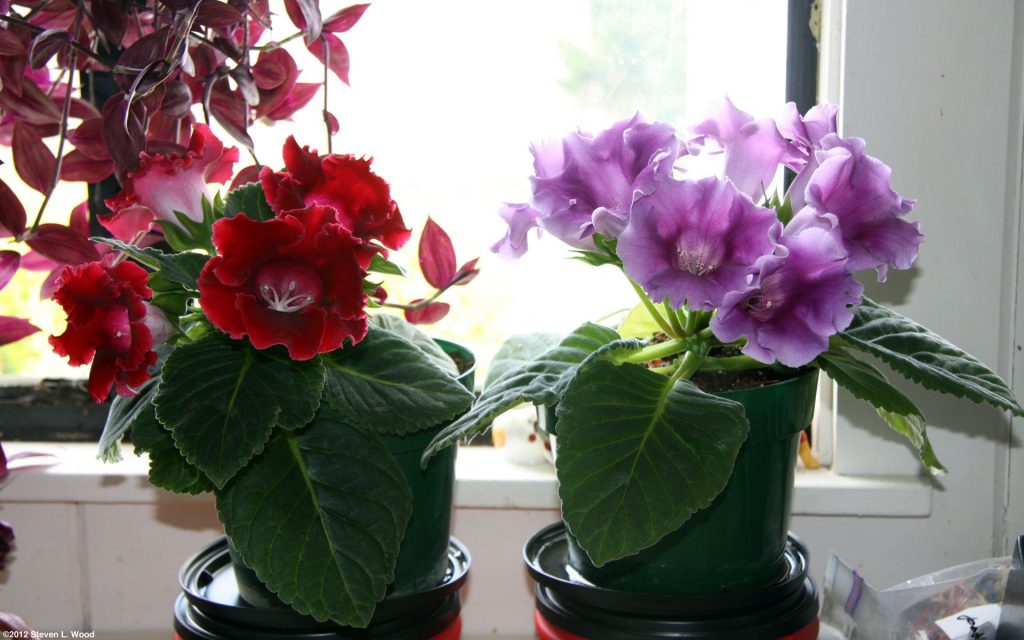



 When gloxinia blooms or grows actively, it needs fertilizer. To do this, you can use ready-made fertilizer for flowering plants, which is poured together with water in the pan. As soon as the plant has faded, feeding should be stopped.
When gloxinia blooms or grows actively, it needs fertilizer. To do this, you can use ready-made fertilizer for flowering plants, which is poured together with water in the pan. As soon as the plant has faded, feeding should be stopped.
Gloxinia after flowering
After the plant has faded, it should gradually stop watering and prepare for a rest period. To do this, Gloxinia is placed in a dark, dry room, where the air temperature does not exceed 13 degrees. As soon as the above-ground part of the plant dries, it must be cut off, leaving a small penechki on the tuber. The tuber itself must be cleaned from the ground and treated with a fungicide. Covering it with perlite or vermiculite, the tuber is placed in a storage box.
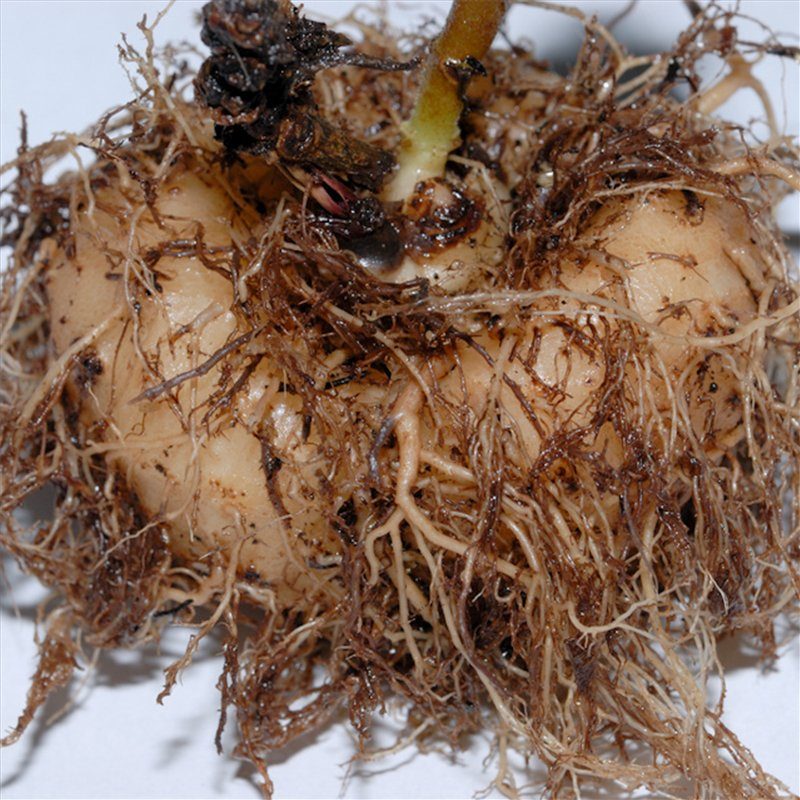
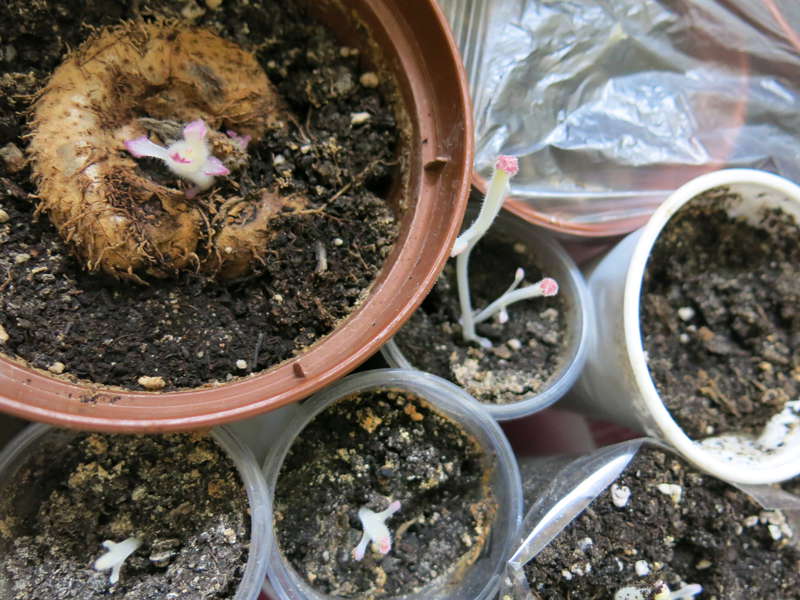


 Several times a month, the surface of perlite is moistened with a fungicide dissolved in water. This will protect the plant tubers from drying out during storage. The rest period of the plant lasts from 1 to 3 months.
Several times a month, the surface of perlite is moistened with a fungicide dissolved in water. This will protect the plant tubers from drying out during storage. The rest period of the plant lasts from 1 to 3 months.
Planting gloxinia
After the rest period, the plant should be transplanted into a new pot. It uses soil for violets or begonias (2 parts of leaf soil and 1 part of sand and humus). At the bottom of the pot you need to lay drainage. It is important that the tuber is only half in the ground.
Reproduction gloxinia
There are several options for breeding gloxinia - by dividing the tubers, cutting and planting seeds of a plant.
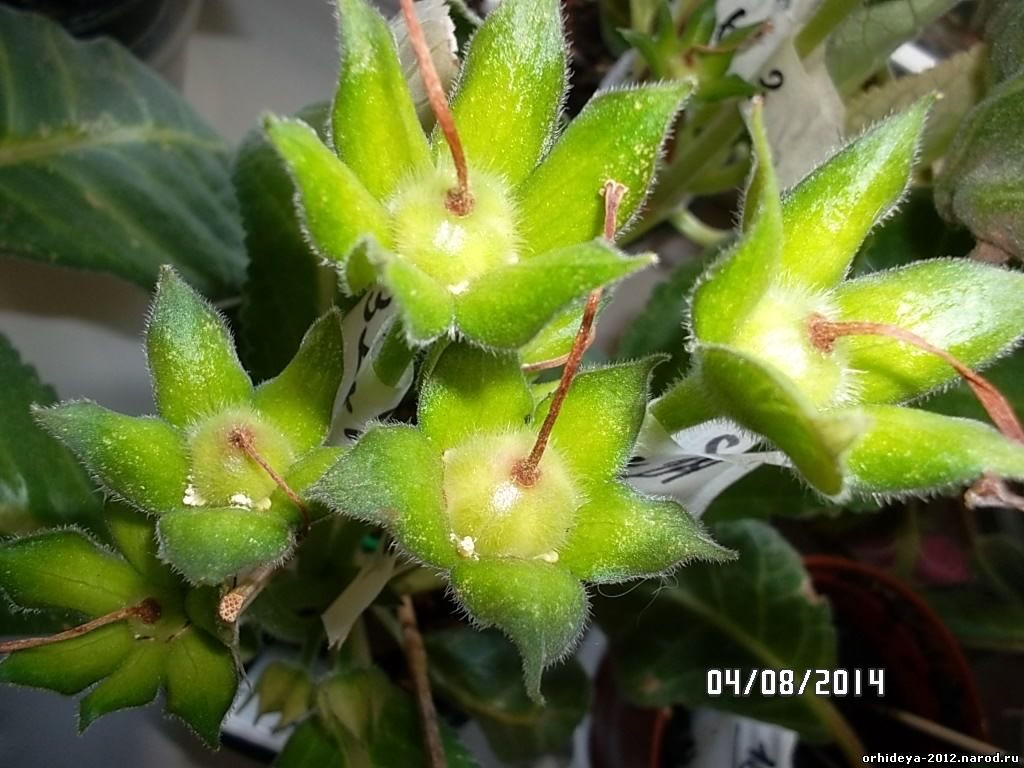
To achieve the appearance of seeds, the plant must be artificially pollinated. Boxes with seeds ripen about 2 months. If you have the opportunity to provide additional lighting to the plant, then you can do it in the period November-April. When this is not possible, the seeds are planted no earlier than February.
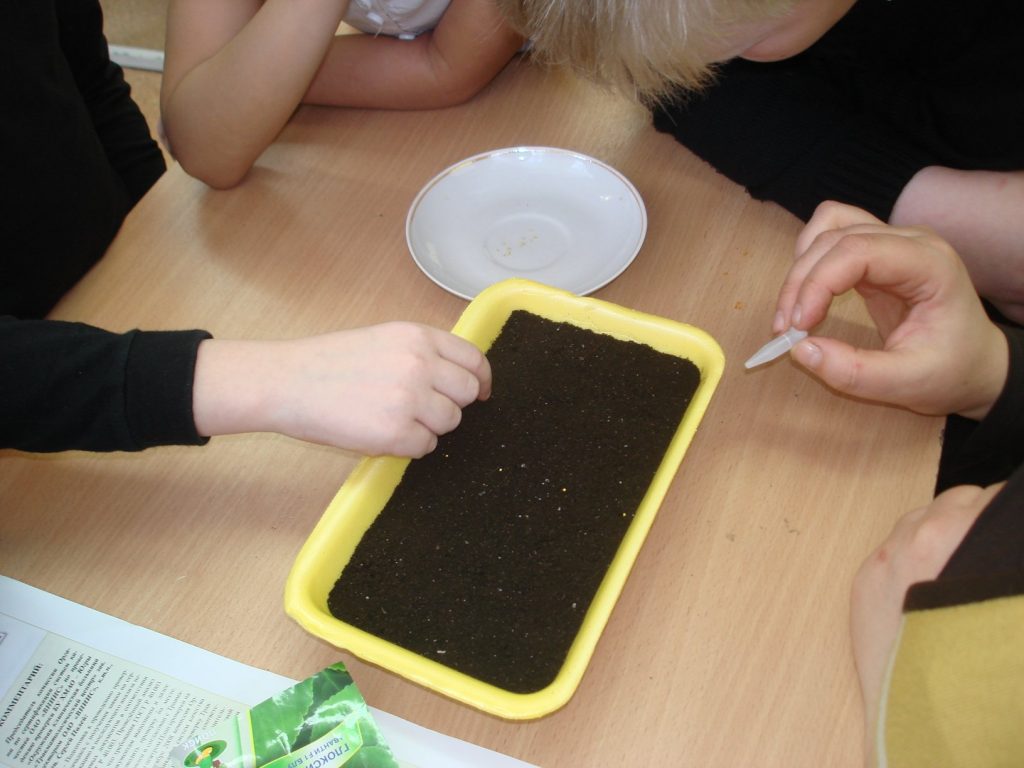
Bury seeds in the ground is not necessary. It is enough to moisten them, cover them with glass and place them in a room with a temperature of about 22 degrees. Every day it is necessary to conduct airing the seeds, slightly raising the glass. If they start to dry, then you need to moisten them additionally.
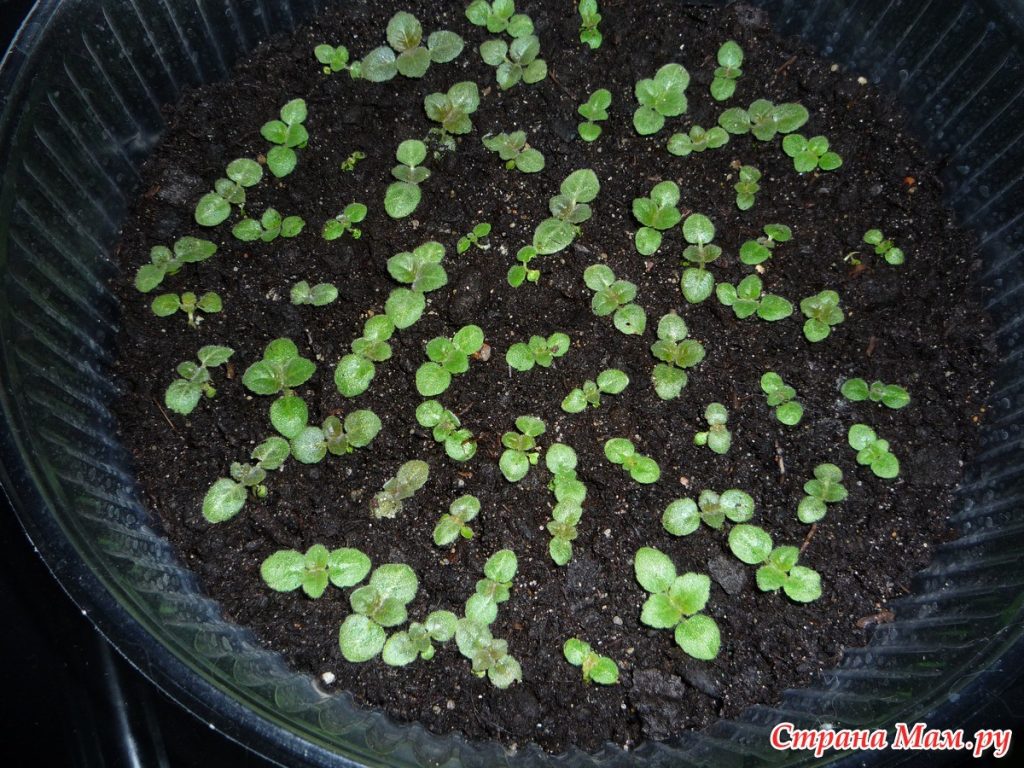
Usually seeds germinate within 10-14 days. After that, the glass is removed, and the seeds are placed in a well-lightened place.
As soon as the first leaf appears, the plant should be dived. After that, the plant is placed in a shaded place at a temperature of about 18-20 degrees. After 6 months, gloxinia should bloom.
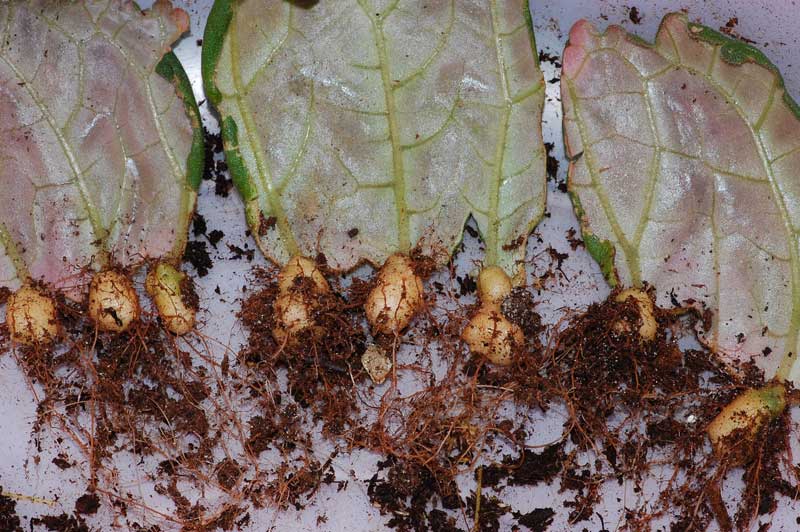
Gloxinia grafting is usually done in summer. To do this, the leaf is cut into 3 parts (middle, lower and upper), and the petiole is removed. Stalk is planted 0.5 cm deep into the sand. From above it is necessary to cover the jar. Rooting requires a temperature of about 23-25 degrees. It is important to regularly moisten the sand. If everything is done correctly, in a few weeks the first roots will appear and the formation of the tuber will begin.
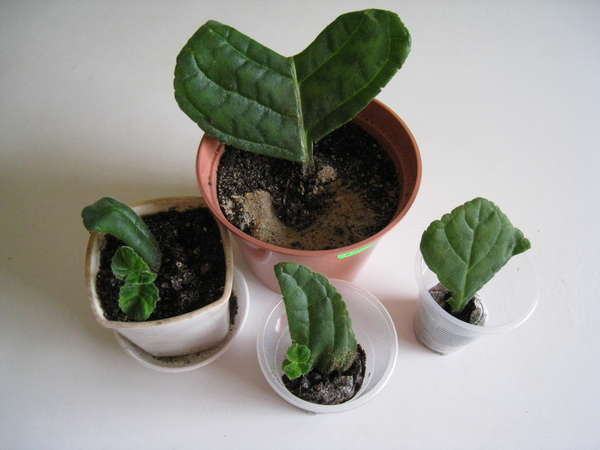
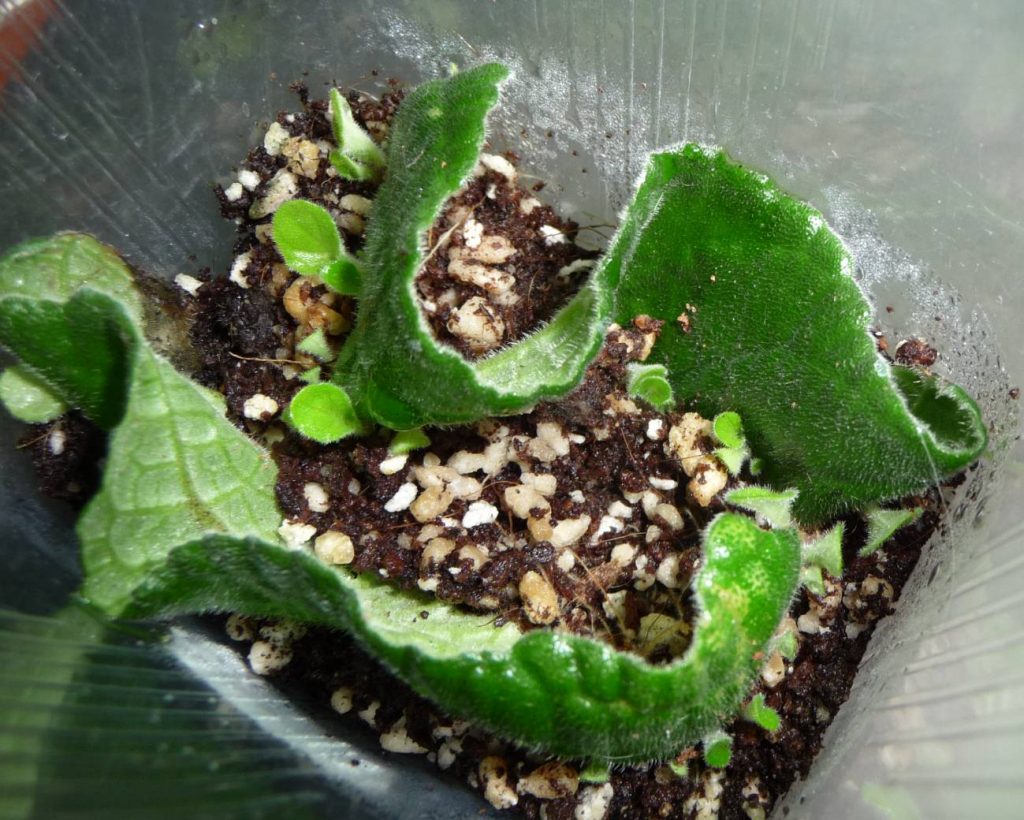

 As soon as the leaf stalk is rooted, it must be transplanted into a pot with a diameter of about 7 cm. With this method of reproduction, gloxinia should bloom in 3 to 4 months.
As soon as the leaf stalk is rooted, it must be transplanted into a pot with a diameter of about 7 cm. With this method of reproduction, gloxinia should bloom in 3 to 4 months.
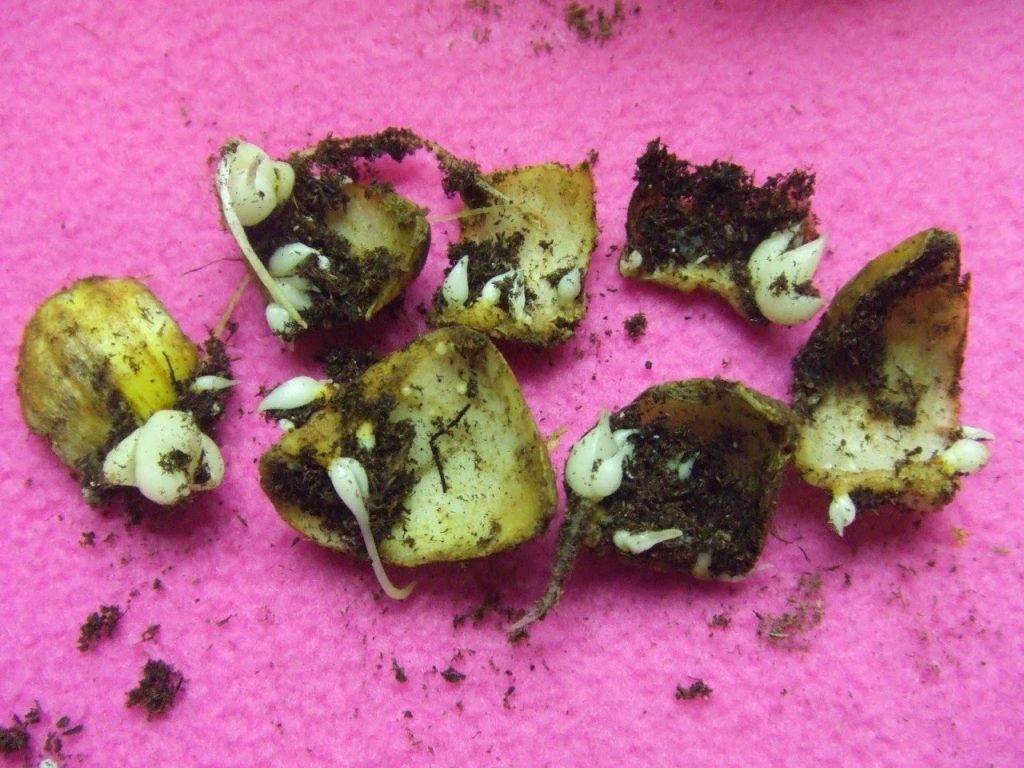
There is also the possibility of plant reproduction by tubers.For this, the tuber is divided into several parts with a sharp knife, and the sections are processed with charcoal. The tuber slices prepared this way are buried in the ground. For their cultivation is suitable temperature of about 20 degrees. After 4-5 months, gloxinia should bloom.
Gloxinia diseases and pests
With the wrong care of the plant it can get sick. Very often, the plant can hit gray rot. Its appearance is the appearance of brown spots on the leaves. In this case, the plant should be treated with a fungicide and remove all damaged leaves.
Another common disease of gloxinia is root rot. At the same time the roots of the plant become brown, and the stem begins to rot at the base. In this case, the plant dies. The cause of the disease can be excessive moisture or watering with cold water.
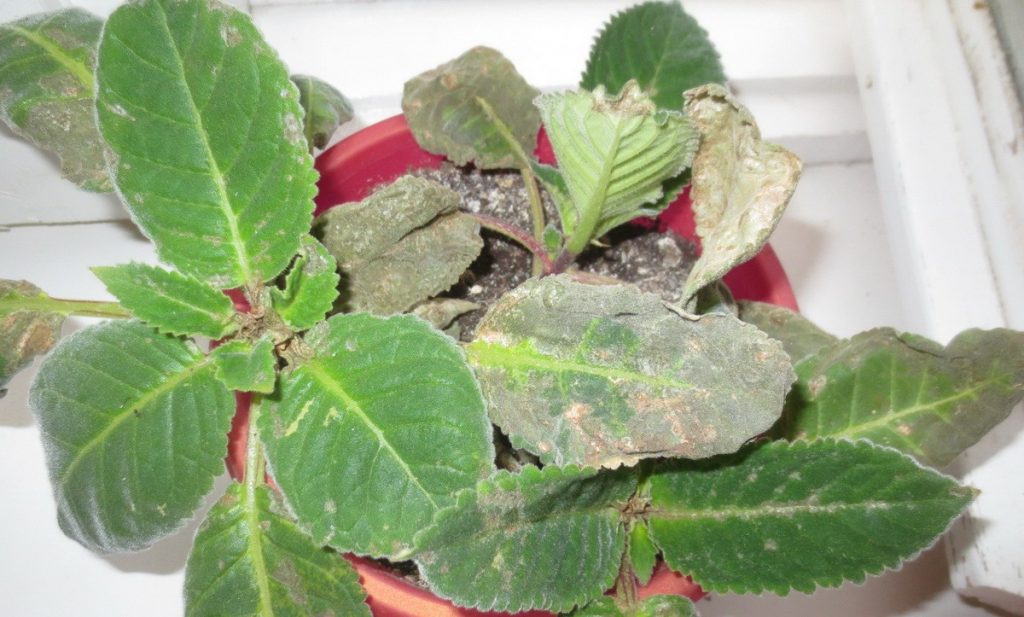
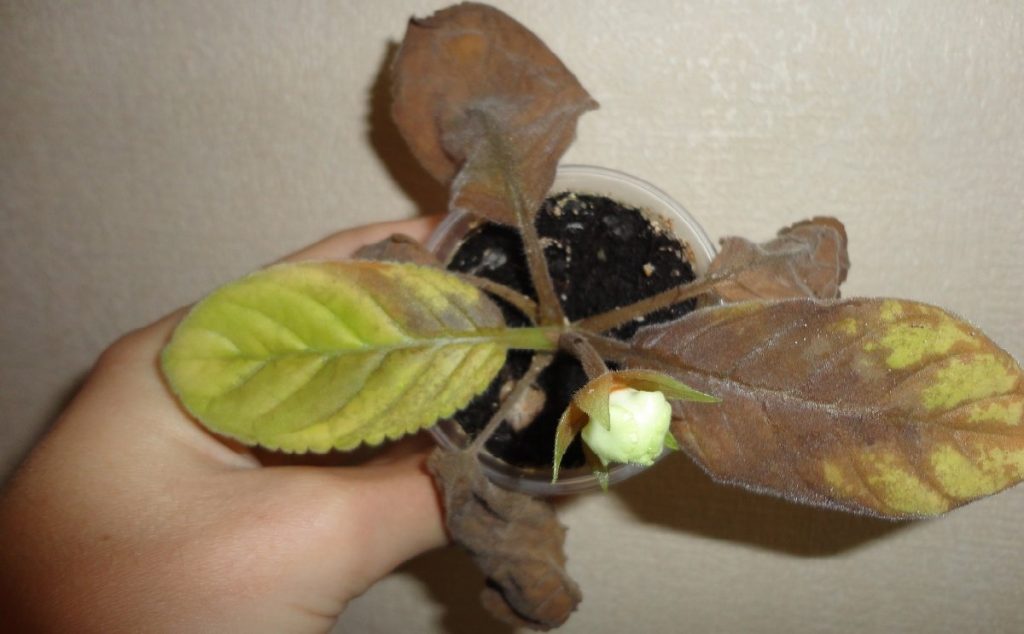
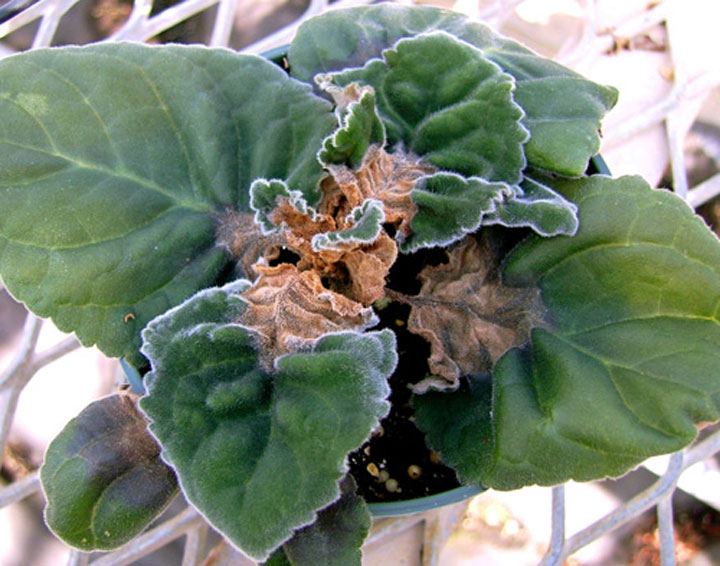

 In addition, gloxinia may suffer from blight, fungus, powdery mildew, or blackleg. These diseases are treated with basezol. But in order to prevent their development, the plant must be periodically treated with phytosporin.
In addition, gloxinia may suffer from blight, fungus, powdery mildew, or blackleg. These diseases are treated with basezol. But in order to prevent their development, the plant must be periodically treated with phytosporin.
Gloxinia can attack various pests. Some of them, for example, cyclamen mite can be detected only by examining a leaf under a microscope. Without it, it is found only if the accumulation of ticks is significant. In this case, on the bottom of the sheet there are areas where a layer of dust is visible. The leaves themselves begin to deform, turn, the stem twists and the flowers wither.
Another almost imperceptible pest is the spider mite. It dwells below the leaf, feeding on its juice. The manifestation of spider mite can become white dots, which eventually turn yellow. If the number of ticks is very large, then on the leaves you can see a web.
If gloxinia was struck by thrips, then dots and strokes begin to appear on its sheets, they gradually dry out. His larvae can penetrate deep into the soil. Therefore, to combat it, the soil should be completely changed, and the plant tuber should be treated with an insecticide (actellic, aktar, fitoverm or karbofos) at least 1 week between treatments.
Gloxinia is a very beautiful and unpretentious plant in the care, able to please you with its flowering up to 6 months.